Ameliorative effects of omega-lycotoxin-Gsp2671e purified from the spider venom of Lycosa praegrandis on memory deficits of glutamate-induced excitotoxicity rat model
- PMID: 36588719
- PMCID: PMC9800828
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1048563
Ameliorative effects of omega-lycotoxin-Gsp2671e purified from the spider venom of Lycosa praegrandis on memory deficits of glutamate-induced excitotoxicity rat model
Abstract
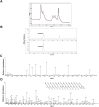
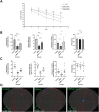
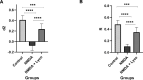
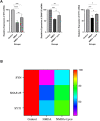
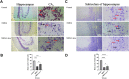
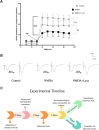
Memory impairment is one of the main complications of Alzheimer's disease (AD). This condition can be induced by hyper-stimulation of N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) of glutamate in the hippocampus, which ends up to pyramidal neurons determination. The release of neurotransmitters relies on voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs) such as P/Q-types. Omega-lycotoxin-Gsp2671e (OLG1e) is a P/Q-type VGCC modulator with high affinity and selectivity. This bio-active small protein was purified and identified from the Lycosa praegrandis venom. The effect of this state-dependent low molecular weight P/Q-type calcium modulator on rats was investigated via glutamate-induced excitotoxicity by N-Methyl-D-aspartate. Also, Electrophysiological amplitude of field excitatory postsynaptic potentials (fEPSPs) in the input-output and Long-term potentiation (LTP) curves were recorded in mossy fiber and the amount of synaptophysin (SYN), synaptosomal-associated protein, 25 kDa (SNAP-25), and synaptotagmin 1(SYT1) genes expression were measured using Real-time PCR technique for synaptic quantification. The outcomes of the current study suggest that OLG1e as a P/Q-type VGCC modulator has an ameliorative effect on excitotoxicity-induced memory defects and prevents the impairment of pyramidal neurons in the rat hippocampus.
Keywords: animal venoms; calcium channel Cav2.1 (P/Q type); calcium channel modulators; memory; spider.
Copyright © 2022 Keimasi, Salehifard, Shahidi, Esmaeili, Mirshah Jafar Esfahani, Beheshti, Amirsadri, Naseri, Keimasi, Ghorbani, Mofid and Moradmand.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Alleviation of cognitive deficits in a rat model of glutamate-induced excitotoxicity, using an N-type voltage-gated calcium channel ligand, extracted from Agelena labyrinthica crude venom.Front Mol Neurosci. 2023 Feb 17;16:1123343. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1123343. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36873105 Free PMC article.
-
The synergic effects of presynaptic calcium channel antagonists purified from spiders on memory elimination of glutamate-induced excitotoxicity in the rat hippocampus trisynaptic circuit.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Nov 30;10:1243976. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1243976. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 38099194 Free PMC article.
-
Purified Native Protein Extracted from the Venom of Agelena orientalis Attenuates Memory Defects in the Rat Model of Glutamate-Induced Excitotoxicity.Protein J. 2023 Oct;42(5):586-595. doi: 10.1007/s10930-023-10140-6. Epub 2023 Aug 2. Protein J. 2023. PMID: 37531037
-
Role of giant depolarizing potentials in shaping synaptic currents in the developing hippocampus.Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2006;18(1-2):13-23. doi: 10.1615/critrevneurobiol.v18.i1-2.30. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2006. PMID: 17725505 Review.
-
[Memory, learning and glutamate receptor].Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 1989 Dec;29(12):1526-8. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 1989. PMID: 2560950 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Alleviation of cognitive deficits in a rat model of glutamate-induced excitotoxicity, using an N-type voltage-gated calcium channel ligand, extracted from Agelena labyrinthica crude venom.Front Mol Neurosci. 2023 Feb 17;16:1123343. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1123343. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36873105 Free PMC article.
-
The synergic effects of presynaptic calcium channel antagonists purified from spiders on memory elimination of glutamate-induced excitotoxicity in the rat hippocampus trisynaptic circuit.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Nov 30;10:1243976. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1243976. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 38099194 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beheshti S., Tohidloo S., Esmaeili A. (2020). Frankincense improves memory retrieval and down-regulates the hippocampal synaptophysin mRNA during the development of the rat brain. Physiol. Pharmacol. 24 (1), 46–53. 10.32598/ppj.24.1.60 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

