Influence of lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase alteration during different pathophysiologic conditions: A 45 years bibliometrics analysis
- PMID: 36588724
- PMCID: PMC9795195
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1062249
Influence of lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase alteration during different pathophysiologic conditions: A 45 years bibliometrics analysis
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Influence of lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase alteration during different pathophysiologic conditions: A 45 years bibliometrics analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jan 12;13:1133686. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1133686. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36712692 Free PMC article.
Abstract
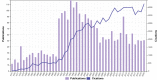
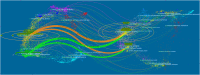
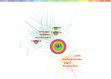
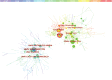
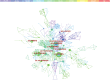
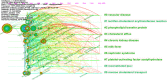
Background: Lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) is an important enzyme responsible for free cholesterol (FC) esterification, which is critical for high density lipoprotein (HDL) maturation and the completion of the reverse cholesterol transport (RCT) process. Plasma LCAT activity and concentration showed various patterns under different physiological and pathological conditions. Research on LCAT has grown rapidly over the past 50 years, but there are no bibliometric studies summarizing this field as a whole. This study aimed to use the bibliometric analysis to demonstrate the trends in LCAT publications, thus offering a brief perspective with regard to future developments in this field. Methods: We used the Web of Science Core Collection to retrieve LCAT-related studies published from 1975 to 2020. The data were further analyzed in the number of studies, the journal which published the most LCAT-related studies, co-authorship network, co-country network, co-institute network, co-reference and the keywords burst by CiteSpace V 5.7. Results: 2584 publications contained 55,311 references were used to analyzed. The number of included articles fluctuated in each year. We found that Journal of lipid research published the most LCAT-related studies. Among all the authors who work on LCAT, they tend to collaborate with a relatively stable group of collaborators to generate several major authors clusters which Albers, J. published the most studies (n = 53). The United States of America contributed the greatest proportion (n = 1036) of LCAT-related studies. The LCAT-related studies have been focused on the vascular disease, lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase reaction, phospholipid, cholesterol efflux, chronic kidney disease, milk fever, nephrotic syndrome, platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase, reconstituted lpa-i, reverse cholesterol transport. Four main research frontiers in terms of burst strength for LCAT-related studies including "transgenic mice", "oxidative stress", "risk", and "cholesterol metabolism "need more attention. Conclusion: This is the first study that demonstrated the trends and future development in LCAT publications. Further studies should focus on the accurate metabolic process of LCAT dependent or independent of RCT using metabolic marker tracking techniques. It was also well worth to further studying the possibility that LCAT may qualify as a biomarker for risk prediction and clinical treatment.
Keywords: bibliometrics; emerging trends; lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase; physiological; risk.
Copyright © 2022 Gao, Wu, Sun, Zhang, Shi, Lu, Qian, Yin, Zhao, Qin and Xue.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) mass; its relationship to LCAT activity and cholesterol esterification rate.J Lipid Res. 1981 Nov;22(8):1206-13. J Lipid Res. 1981. PMID: 7320631
-
Acquired lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency as a major factor in lowering plasma HDL levels in chronic kidney disease.J Intern Med. 2015 May;277(5):552-61. doi: 10.1111/joim.12290. Epub 2014 Aug 1. J Intern Med. 2015. PMID: 25039266
-
Overexpression of human lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase leads to hyperalphalipoproteinemia in transgenic mice.J Biol Chem. 1995 May 19;270(20):12269-75. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.20.12269. J Biol Chem. 1995. PMID: 7744879
-
Lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase, high-density lipoproteins, and atheroprotection in humans.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2010 Feb;20(2):50-3. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2010.03.007. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2010. PMID: 20656215 Review.
-
The role of lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase in the modulation of cardiometabolic risks - a clinical update and emerging insights from animal models.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Apr;1821(4):654-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2011.12.012. Epub 2012 Jan 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22326749 Review.
Cited by
-
Yoga Therapy Attenuates the Progression of Diabetes - Insights from Proteomics and Metabolomics Analysis.Int J Yoga. 2024 Sep-Dec;17(3):163-174. doi: 10.4103/ijoy.ijoy_178_24. Epub 2024 Dec 14. Int J Yoga. 2024. PMID: 39959515 Free PMC article.
-
Visualization of breast cancer-related protein synthesis from the perspective of bibliometric analysis.Eur J Med Res. 2023 Oct 27;28(1):461. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01364-4. Eur J Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37885035 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Unsaturated Fatty Acid-Type Diet and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analyses.Nutrients. 2024 Jun 20;16(12):1974. doi: 10.3390/nu16121974. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38931327 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anantharamaiah G. M., Jones J. L., Brouillette C. G., Schmidt C. F., Chung B. H., Hughes T. A., et al. (1985). Studies of synthetic peptide analogs of the amphipathic helix. Structure of complexes with dimyristoyl phosphatidylcholine. J. Biol. Chem. 260, 10248–10255. 10.1016/s0021-9258(17)39238-4 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

