Nuclear imaging for localization and surgical outcome prediction in epilepsy: A review of latest discoveries and future perspectives
- PMID: 36588897
- PMCID: PMC9800996
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2022.1083775
Nuclear imaging for localization and surgical outcome prediction in epilepsy: A review of latest discoveries and future perspectives
Abstract
Background: Epilepsy is one of the most common neurological disorders. Approximately, one-third of patients with epilepsy have seizures refractory to antiepileptic drugs and further require surgical removal of the epileptogenic region. In the last decade, there have been many recent developments in radiopharmaceuticals, novel image analysis techniques, and new software for an epileptogenic zone (EZ) localization.
Objectives: Recently, we provided the latest discoveries, current challenges, and future perspectives in the field of positron emission tomography (PET) and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) in epilepsy.
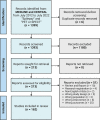
Methods: We searched for relevant articles published in MEDLINE and CENTRAL from July 2012 to July 2022. A systematic literature review based on the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis was conducted using the keywords "Epilepsy" and "PET or SPECT." We included both prospective and retrospective studies. Studies with preclinical subjects or not focusing on EZ localization or surgical outcome prediction using recently developed PET radiopharmaceuticals, novel image analysis techniques, and new software were excluded from the review. The remaining 162 articles were reviewed.
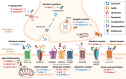
Results: We first present recent findings and developments in PET radiopharmaceuticals. Second, we present novel image analysis techniques and new software in the last decade for EZ localization. Finally, we summarize the overall findings and discuss future perspectives in the field of PET and SPECT in epilepsy.
Conclusion: Combining new radiopharmaceutical development, new indications, new techniques, and software improves EZ localization and provides a better understanding of epilepsy. These have proven not to only predict prognosis but also to improve the outcome of epilepsy surgery.
Keywords: PET; SPECT; epilepsy; nuclear medicine; presurgical localization; radiopharmaceuticals; techniques.
Copyright © 2022 Sukprakun and Tepmongkol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neuronuclear assessment of patients with epilepsy.Semin Nucl Med. 2008 Jul;38(4):227-39. doi: 10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2008.02.004. Semin Nucl Med. 2008. PMID: 18514079 Review.
-
[PET and SPECT in epilepsy].Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2014 May-Jun;33(3):165-74. doi: 10.1016/j.remn.2014.01.001. Epub 2014 Feb 22. Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2014. PMID: 24565567 Review. Spanish.
-
The effect of injection time on rates of epileptogenic zone localization using SISCOM and STATISCOM.Epilepsy Behav. 2021 May;118:107945. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2021.107945. Epub 2021 Apr 10. Epilepsy Behav. 2021. PMID: 33845344
-
Comparison of MR imaging with PET and ictal SPECT in 118 patients with intractable epilepsy.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999 Apr;20(4):593-9. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999. PMID: 10319968 Free PMC article.
-
[Nuclear medicine imaging: new radiotracers and future techniques].Neurochirurgie. 2008 May;54(3):231-5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuchi.2008.02.035. Epub 2008 Apr 28. Neurochirurgie. 2008. PMID: 18440564 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Hypometabolic patterns of focal cortical dysplasia in PET-MRI co-registration imaging: a retrospective evaluation in a series of 83 patients.Front Neurosci. 2023 Sep 25;17:1173534. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1173534. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37817803 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative SISCOM assessment for epileptogenic zone localization: insights from a multicenter study comparing two software platforms in temporal lobe epilepsy.Front Neurol. 2025 Apr 15;16:1552774. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1552774. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40303886 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Luders HO, Najm I, Nair D, Widdess-Walsh P, Bingman W. The epileptogenic zone: general principles. Epileptic Disorders Int Epilepsy J Videotape. (2006) 8:S1–9. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

