Effect of nutrients deficiency on biofilm formation and single cell protein production with a purple non-sulphur bacteria enriched culture
- PMID: 36588982
- PMCID: PMC9794892
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioflm.2022.100098
Effect of nutrients deficiency on biofilm formation and single cell protein production with a purple non-sulphur bacteria enriched culture
Abstract
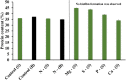
Purple non-sulphur bacteria (PNSB) are of interest for biorefinery applications to create biomolecules, but their production cost is expensive due to substrate and biomass separation costs. This research has utilized fuel synthesis wastewater (FSW) as a low-cost carbon-rich substrate to produce single-cell protein (SCP) and examines PNSB biofilm formation using this substrate to achieve a more efficient biomass-liquid separation. In this study, PNSB were grown in Ca, Mg, S, P, and N-deficient media using green shade as biofilm support material. Among these nutrient conditions, only N-deficient and control (nutrient-sufficient) conditions showed biofilm formation. Although total biomass growth of the control was 1.5 times that of the N-deficient condition and highest overall, the total biofilm-biomass in the N-deficient condition was 2.5 times greater than the control, comprising 49% of total biomass produced. Total protein content was similar between these four biomass samples, ranging from 35.0 ± 0.2% to 37.2 ± 0.0%. The highest protein content of 44.7 ± 1.3% occurred in the Mg-deficient condition (suspended biomass only) but suffered from a low growth rate. Overall, nutrient sufficient conditions are optimal for overall protein productivity and dominated by suspended growth, but where fixed growth systems are desired for cost-effective harvesting, N-deficient conditions provide an effective means to maximize biofilm production without sacrificing protein content.
Keywords: Biofilm; COD, Chemical oxygen demand; FSW, Fuel synthesis wastewater; Fuel-synthesis wastewater; Nutrients deficiency; PNSB, Purple non-sulfur bacteria; Purple non-sulphur bacteria; SCP, Single cell protein; SEM, Scanning electron microscope; Single cell protein; TS, Total solids.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures








References
-
- Duarte E., Fragoso R., Smozinski N., Tavares J. Enhancing bioenergy recovery from agro-food biowastes as a strategy to promote circular bioeconomy. J Sustain Dev Energy, Water Environ Syst. 2021;9:1–13. doi: 10.13044/j.sdewes.d8.0320. - DOI
-
- Akroum-Amrouche D., Abdi N., Lounici H., Mameri N. Proc 2013 International Renewable Sustainable Energy Conference. IRSEC 2013; 2013. Biohydrogen production by dark and photo-fermentation processes; pp. 499–503. - DOI
-
- Jafari A., Esmaeilzadeh F., Mowla D., Sadatshojaei E., Heidari S., Wood D.A. New insights to direct conversion of wet microalgae impregnated with ethanol to biodiesel exploiting extraction with supercritical carbon dioxide. Fuel. 2021;285 doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.119199. - DOI
-
- Matassa S., Papirio S., Pikaar I., Hülsen T., Leijenhorst E., Esposito G., et al. Upcycling of biowaste carbon and nutrients in line with consumer confidence: the “full gas” route to single cell protein. Green Chem. 2020;22:4912–4929. doi: 10.1039/d0gc01382j. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

