Cardiogenic shock due to arrhythmia-induced cardiomyopathy and its recovery after radiofrequency ablation under extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support
- PMID: 36588999
- PMCID: PMC9795292
- DOI: 10.1016/j.hroo.2022.10.006
Cardiogenic shock due to arrhythmia-induced cardiomyopathy and its recovery after radiofrequency ablation under extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support
Keywords: Atrial tachycardia; Cardiogenic shock; Catheter ablation; ECMO; Tachycardiomyopathy.
Figures
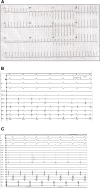


References
-
- Medi C., Kalman J., Haqqani H. Tachycardia-mediated cardiomyopathy secondary to focal atrial tachycardia: long-term outcome after catheter ablation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;53:1791–1797. - PubMed
-
- Whipple G.H., Sheffield L., Woodman E. Reversible congestive heart failure due to chronic rapid stimulation of the normal heart. Pro N Engl Cardiovasc Soc. 1962;20:39–40.
-
- Brugada J., Katritsis D., Arbelo E., et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the management of patients with supraventricular tachycardia: the Task Force for the management of patients with supraventricular tachycardia of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Eur Heart J. 2020;41:655–720. - PubMed
-
- Scherrer V., Lasgi C., Hariri S., et al. Radiofrequency ablation under extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for atrial tachycardia in postpartum. J Card Surg. 2012;27:647–649. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

