Remote monitoring of pacemakers and defibrillators: Effective and safe in Brazil?
- PMID: 36589013
- PMCID: PMC9795284
- DOI: 10.1016/j.hroo.2022.10.001
Remote monitoring of pacemakers and defibrillators: Effective and safe in Brazil?
Abstract
Background: The remote monitoring (RM) of cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIEDs) has become a common method of in-home monitoring and follow-up in high-income countries given its effectiveness, safety, convenience, and the possibility of early intervention. However, in Brazil, RM is still underutilized.
Objectives: This observational study aims to demonstrate our experience of using RM in Brazil and the predictive factors of RM of CIED follow-up in Brazil.
Methods: This was a prospective cohort study of patients with a CIED. Event rates are reported and clinical responses to those findings and outcomes based on the detection of RM. A logistic regression model was performed to identify predictors of more events, with P < .05 for statistical significance.
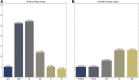
Results: This study evaluated consecutive 119 patients: 30.2% with pacemakers, 42.8% with implantable cardioverter-defibrillator, 22.7% with cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) with defibrillator, and 3.3% with CRT with pacemaker. Events were detected in 63.9% of the cases in 29.5 ± 23 months of follow-up. The outcomes found were that 44.5% needed elective evaluation in medical treatment and 23.5% needed immediate evaluation in therapy. Logistic regression analysis showed that the groups with CRT or CRT with defibrillator (75.0%), reduced ejection fraction (76.5%), and New York Heart Association functional class ≥II (75.0%) had the highest RM event rates.
Conclusions: RM proved to be effective and safe in the follow-up of patients with CIEDs in Brazil, allowing early interventions and facilitating therapeutic management.
Keywords: Brazil; Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator; Middle-income countries; Pacemaker; Remote monitoring.
© 2022 Heart Rhythm Society. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Slotwiner D., Varma N., Akar J.G., et al. HRS Expert Consensus Statement on remote interrogation and monitoring for cardiovascular implantable electronic devices. Heart Rhythm. 2015;12:e69–e100. - PubMed
-
- Yee R., Verma A., Beardsall M., Fraser J., Philippon F., Exner D.V. Canadian Cardiovascular Society/Canadian Heart Rhythm Society Joint Position Statement on the use of remote monitoring for cardiovascular implantable electronic device follow-up. Can J Cardiol. 2013;29:644–651. - PubMed
-
- Wilkoff B.L., Auricchio A., Brugada J., et al. HRS/EHRA Expert Consensus on the monitoring of cardiovascular implantable electronic devices (CIEDs): description of techniques, indications, personnel, frequency and ethical considerations. Heart Rhythm. 2008;5:907–925. - PubMed
-
- Crossley G.H., Boyle A., Vitense H., Chang Y., Hardwin Mead R. The CONNECT (Clinical Evaluation of Remote Notification to Reduce Time to Clinical Decision) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;57:1181–1189. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

