Effect of Hydroalcoholic Extract of Stachys lavandulifolia on Pentylenetetrazole-induced Seizures in Male Mice: The Role of GABAergic and Opioidergic Systems
- PMID: 36589024
- PMCID: PMC9790098
- DOI: 10.32598/bcn.2021.2299.1
Effect of Hydroalcoholic Extract of Stachys lavandulifolia on Pentylenetetrazole-induced Seizures in Male Mice: The Role of GABAergic and Opioidergic Systems
Abstract
Introduction: Epilepsy is one of the most common neurological disorders. Though there are several effective drugs for treating epilepsy, most drugs are associated with side effects and drug interactions. Stachys lavandulifolia used in Iranian traditional medicine has proven anti-anxiety and sedative properties. The current study aimed to evaluate the anticonvulsant effect of hydroalcoholic extract of S. lavandulifoliaon the Pentylenetetrazole (PTZ)-induced seizure in male mice and the role of benzodiazepine and opioid receptors.
Methods: This study was conducted on 100 male mice, randomly categorized into 10 groups: Normal Saline (NS), two diazepam groups (0.025 and 0.1 mg/kg), three S. lavandulifolia extract groups (50, 100, and 200 mg/kg), diazepam 0.025 mg/kg+S. lavandulifolia extract 50 mg/kg, and three groups that pretreated with NS, flumazenil, or naloxone, 5 min before injection of 200 mg/kg S. lavandulifolia extract. After 30 min, PTZ (80 mg/kg) was injected into animals, and seizure indices were evaluated.
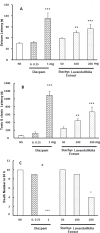
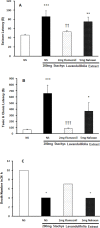
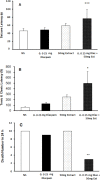
Results: The S. lavandulifoliaextract attenuated the PTZ-induced seizures in a dose-dependent manner, and pretreatment with flumazenil reversed this effect. However, pretreatment with naloxone could not reverse this effect because seizure indices in the naloxone pretreated group were lower than that in the normal saline group. The combination of an ineffective dose of diazepam and S. lavandulifoliaextract decreased PTZ-induced seizures.
Conclusion: The results of our study showed the anticonvulsant properties of hydroalcoholic extract of S. lavandulifolia. These effects might be due to the impact of the components of this extract on the central benzodiazepine system.
Highlights: Hydroalcoholic extract of S. lavandulifolia attenuated the PTZ-induced seizures in a dose dependent manner.Pretreatment with flumazenil (blocker of benzodiazepines receptor) reversed anti-seizure effect of S. lavandulifolia extract.Combination of an ineffective dose of diazepam and S. lavandulifolia extract decreased PTZ-induced seizures.
Plain language summary: Epilepsy is one of the most common neurological disorders after stroke and is characterized by recurrent seizures due to abnormal excessive neural activity in the brain. Although there are many anticonvulsant drugs on the market, not all patients with epilepsy can be treated and one-third of patients suffer from recurring epilepsy despite using different antiepileptic drugs and more than 50% of them show side effects drugs during treatment. So, it is necessary to conduct further studies to develop more effective anti-epilepsy drugs with the minimum side effects. In recent years, plenty of studies have been conducted on medical plants, and S. lavandulifolia reported among the Iranian traditional medicine with antianxiety and sedative features. Some studies have mentioned the sedative and anti-inflammatory function of S. lavandulifolia, and its significant effects on anxiety have been approved comparable to diazepam. Overall, considering the anti-anxiety, analgesic, and sedative effects of the hydroalcoholic extract of S. lavandulifolia, it might possess anti-convulsive effects, too. The purpose of the current study was designed to investigate whether the effect of intra peritoneal injection of hydroalcoholic extract of S. lavandulifolia on the PTZ-induced convulsion in male mice and assessed the role of benzodiazepine and opioid receptors. Results of this study demonstrated that S. lavandulifolia extract attenuated the PTZ-induced seizures in a dose dependent manner, and pretreatment with flumazenil (blocker of benzodiazepines receptor) reversed this effect. However, pretreatment with naloxone (Non-selective blocker of opioids receptor) could not reverse this effect but the combination of an ineffective dose of diazepam and S. lavandulifolia extract decreased PTZ-induced seizures, thus anti-epileptic effect of S. lavandulifolia mediated by benzodiazepine receptors.
Keywords: Flumazenil; Naloxone; Pentylenetetrazole; Seizure; Stachys lavandulifolia.
Copyright© 2022 Iranian Neuroscience Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of the non-NMDA antagonists NBQX and the 2,3-benzodiazepine GYKI 52466 on different seizure types in mice: comparison with diazepam and interactions with flumazenil.Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Dec;113(4):1349-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb17146.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1994. PMID: 7889291 Free PMC article.
-
Anticonvulsant Effects of the Hydroalcoholic Extract of Alpinia officinarum Rhizomesin Mice: Involvement of Benzodiazepine and Opioid Receptors.J Epilepsy Res. 2017 Jun 30;7(1):33-38. doi: 10.14581/jer.17006. eCollection 2017 Jun. J Epilepsy Res. 2017. PMID: 28775953 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Satureja Bachtiarica Essential Oil in Preventing Seizure in Pentylenetetrazol-Kindled Mice.Basic Clin Neurosci. 2022 Jul-Aug;13(4):465-475. doi: 10.32598/bcn.2021.1665.1. Epub 2022 Jul 1. Basic Clin Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36561234 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental Models for the Discovery of Novel Anticonvulsant Drugs: Focus on Pentylenetetrazole-Induced Seizures and Associated Memory Deficits.Curr Pharm Des. 2020;26(15):1693-1711. doi: 10.2174/1381612826666200131105324. Curr Pharm Des. 2020. PMID: 32003682 Review.
-
Herbal nanoparticles: bridging traditional medicine and modern science in epilepsy treatment.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 May 7. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04239-z. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40332554 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Rosiglitazone, the Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor (PPAR)-γ Agonist, on Apoptosis, Inflammatory Cytokines and Oxidative Stress in pentylenetetrazole-Induced Seizures in Kindled Mice.Neurochem Res. 2023 Sep;48(9):2870-2880. doi: 10.1007/s11064-023-03951-7. Epub 2023 May 19. Neurochem Res. 2023. PMID: 37204549
References
-
- Bahmani M., Karamati S. A., Hassanzadazar H., Forouzan S., Rafieian-Kopaei M., Kazemi-Ghoshchi B., et al. (2014). Ethnobotanic study of medicinal plants in Urmia city: Identification and traditional using of antiparasites plants. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Disease, 4, S906–10. [DOI:10.1016/S2222-1808(14)60756-8] - DOI
-
- Bahramnjead E., Roodsari S. K., Rahimi N., Etemadi P., Aghaei I., Dehpour A. R. (2018). Effects of modafinil on clonic seizure threshold induced by pentylenetetrazole in mice: Involvement of glutamate, nitric oxide, GABA, and serotonin pathways. Neurochemical Research, 43(11), 2025–37. [DOI:10.1007/s11064-018-2623-7] [PMID ] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Delfan B., Bahmani M., Rafieian-Kopaei M., Delfan M., Saki K. (2014). A review study on ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants used in relief of toothache in Lorestan Province, Iran. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Disease, 4, S879–84. [DOI:10.1016/S2222-1808(14)60751-9] - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
