Oculomotor Cranial Neuropathies: Diagnosis and Management
- PMID: 36589037
- PMCID: PMC9795710
- DOI: 10.4103/aian.aian_167_22
Oculomotor Cranial Neuropathies: Diagnosis and Management
Abstract
Ocular nerve palsies are among the most common cranial neuropathies in neurological practice. Nerves can get affected anywhere along their path from the brainstem to the orbit. There can be isolated involvement of multiple cranial nerves together. The etiologies differ according to the type of presentation. The steps toward the diagnosis need to be strategically planned and must be based on clinical localization. It is crucial to make proper localization to plan further investigations and thus treatment of the etiology. This review covers the approach toward the diagnosis, etiologies involved, and management of ocular cranial neuropathies.
Keywords: Abducens palsy; diplopia; ocular nerve palsy; oculomotor palsy; trochlear palsy.
Copyright: © 2022 Annals of Indian Academy of Neurology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
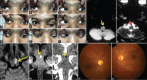


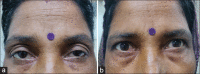
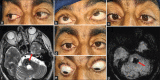


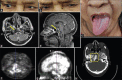
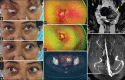
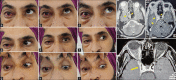

References
-
- Brazis PW, Masdeu JC, Biller J, editors. The localization of lesions affecting the ocular motor system. Localization in Clinical Neurology. (7th) 2017:187–334.
-
- Laine FJ. Cranial nerves III, IV, and VI. Top Magn Reson Imaging. 1996;8:111–30. - PubMed
-
- Büttner-Ennever JA. The extraocular motor nuclei: Organization and functional neuroanatomy. Prog Brain Res. 2006;151:95–125. - PubMed
-
- Martins C, Yasuda A, Campero A, Rhoton AL., Jr Microsurgical anatomy of the oculomotor cistern. Neurosurgery. 2006;58(4 Suppl 2) ONS-220-7; discussion ONS-7-8. - PubMed
-
- Miller NR. The ocular motor nerves. Curr Opin Neurol. 1996;9:21–5. - PubMed

