Spatiotemporal singular value decomposition for denoising in photoacoustic imaging with a low-energy excitation light source
- PMID: 36589568
- PMCID: PMC9774869
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.471198
Spatiotemporal singular value decomposition for denoising in photoacoustic imaging with a low-energy excitation light source
Abstract
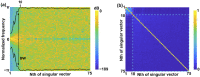
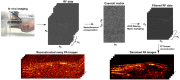
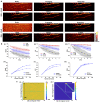
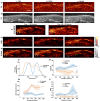
Photoacoustic (PA) imaging is an emerging hybrid imaging modality that combines rich optical spectroscopic contrast and high ultrasonic resolution, and thus holds tremendous promise for a wide range of pre-clinical and clinical applications. Compact and affordable light sources such as light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and laser diodes (LDs) are promising alternatives to bulky and expensive solid-state laser systems that are commonly used as PA light sources. These could accelerate the clinical translation of PA technology. However, PA signals generated with these light sources are readily degraded by noise due to the low optical fluence, leading to decreased signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) in PA images. In this work, a spatiotemporal singular value decomposition (SVD) based PA denoising method was investigated for these light sources that usually have low fluence and high repetition rates. The proposed method leverages both spatial and temporal correlations between radiofrequency (RF) data frames. Validation was performed on simulations and in vivo PA data acquired from human fingers (2D) and forearm (3D) using a LED-based system. Spatiotemporal SVD greatly enhanced the PA signals of blood vessels corrupted by noise while preserving a high temporal resolution to slow motions, improving the SNR of in vivo PA images by 90.3%, 56.0%, and 187.4% compared to single frame-based wavelet denoising, averaging across 200 frames, and single frame without denoising, respectively. With a fast processing time of SVD (∼50 µs per frame), the proposed method is well suited to PA imaging systems with low-energy excitation light sources for real-time in vivo applications.
Published by Optica Publishing Group under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License. Further distribution of this work must maintain attribution to the author(s) and the published article’s title, journal citation, and DOI.
Conflict of interest statement
T.V. is co-founder and shareholder of Hypervision Surgical Ltd, London, UK. He is also a shareholder of Mauna Kea Technologies, Paris, France.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
