Resilience assessment of metro stations against rainstorm disaster based on cloud model: a case study in Chongqing, China
- PMID: 36589619
- PMCID: PMC9786533
- DOI: 10.1007/s11069-022-05765-2
Resilience assessment of metro stations against rainstorm disaster based on cloud model: a case study in Chongqing, China
Abstract
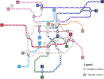
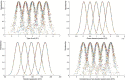
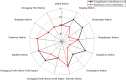
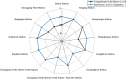
Extremely heavy rainfall has posed a significant hazard to urban growth as the most common and disaster-prone natural calamity. Due to its unique geographical location, the metro system is more vulnerable to waterlogging caused by rainstorm disaster. Research on resilience to natural disasters has attracted extensive attention in recent years. However, few studies have focused on the resilience of the metro system against rainstorms. Therefore, this paper aims to develop an assessment model for evaluating metro stations' resilience levels. Twenty factors are carried out from dimensions of resistance, recovery and adaptation. The methods of ordered binary comparison, entropy weight and cloud model are proposed to build the assessment model. Then, taking Chongqing metro system in china as a case study, the resilience level of 13 metro stations is calculated. Radar charts from dimensions of resistance, recovery, and adaptation are created to propose recommendations for improving metro stations' resilience against rainstorms, providing a reference for the sustainable development of the metro system. The case study of the Chongqing metro system in china demonstrates that the assessment model can effectively evaluate the resilience level of metro stations and can be used in other infrastructures under natural disasters for resilience assessment.
Keywords: Assessment; Cloud model; Metro stations; Rainstorm disaster; Resilience.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature B.V. 2022, Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Flood resilience assessment of metro station entrances based on the PSR model framework: A case study of the Donghaochong Basin, Guangzhou.J Environ Manage. 2024 Aug;366:121922. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.121922. Epub 2024 Jul 20. J Environ Manage. 2024. PMID: 39033619
-
A research on urban disaster resilience assessment system for rainstorm and flood disasters: A case study of Beijing.PLoS One. 2023 Oct 26;18(10):e0291674. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0291674. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37883466 Free PMC article.
-
A network-based framework for assessing infrastructure resilience: a case study of the London metro system.J R Soc Interface. 2016 May;13(118):20160113. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2016.0113. J R Soc Interface. 2016. PMID: 27146689 Free PMC article.
-
A Scientometric Review of Urban Disaster Resilience Research.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Apr 1;18(7):3677. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18073677. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33916024 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of the Literature on Community Resilience and Disaster Recovery.Curr Environ Health Rep. 2019 Sep;6(3):167-173. doi: 10.1007/s40572-019-00239-3. Curr Environ Health Rep. 2019. PMID: 31267349 Review.
Cited by
-
The tight balance state and mechanism of disaster-resilient resources in karst small towns: a Chinese karst landform case study.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 4;15(1):758. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-85107-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39755824 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aoki Y, Yoshizawa A, Taminato T. Anti-inundation measures for underground stations of Tokyo metro. Proc Eng. 2016;165:2–10. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2016.11.730. - DOI
-
- Blake ES, Kimberlain TB, Berg RJ, et al. Tropical cyclone report: hurricane sandy. Nat Hurr Center. 2013;12:1–10.
-
- Chen CK, Xu LL, Zhao DY, et al. A new model for describing the urban resilience considering adaptability, resistance and recovery. Saf Sci. 2020;128:104756. doi: 10.1016/j.ssci.2020.104756. - DOI
-
- Chen ZL, He QY, Su XC, et al. The opening conditions of the metro and its early characteristics: a historical perspective. Tunn Undergr Space Technol. 2021;108:103732. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2020.103732. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
