Comparable Effects of Sleeve Gastrectomy and Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass on Basal Fuel Metabolism and Insulin Sensitivity in Individuals with Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 36589629
- PMCID: PMC9798105
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5476454
Comparable Effects of Sleeve Gastrectomy and Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass on Basal Fuel Metabolism and Insulin Sensitivity in Individuals with Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
Aim: Bariatric surgery improves insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance in obese individuals with type 2 diabetes (T2D), but there is a lack of data comparing the underlying metabolic mechanisms after the 2 most common surgical procedures Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery (RYGB) and sleeve gastrectomy (SG). This study was designed to assess and compare the effects of RYGB and SG on fuel metabolism in the basal state and insulin sensitivity during a two-step euglycemic glucose clamp.
Materials and methods: 16 obese individuals with T2D undergoing either RYGB (n = 9) or SG (n = 7) were investigated before and 2 months after surgery, and 8 healthy individuals without obesity and T2D served as controls. All underwent a 2 h basal study followed by a 5 h 2-step hyperinsulinemic euglycemic glucose clamp at insulin infusion rates of 0.5 and 1.0 mU/kg LBM/min.
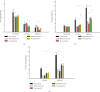
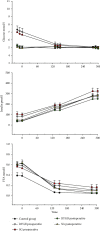
Results: RYGB and SG induced comparable 15% weight losses, normalized HbA1c, fasting glucose, fasting insulin, and decreased energy expenditure. In parallel, we recorded similar increments (about 100%) in overall insulin sensitivity (M-value) and glucose disposal and similar decrements (about 50%) in endogenous glucose production and FFA levels during the clamp; likewise, basal glucose and insulin concentrations decreased proportionally.
Conclusion: Our data suggest that RYGB and SG improve basal fuel metabolism and two-step insulin sensitivity in the liver, muscle, and fat and seem equally favourable when investigated 2 months after surgery. This trial is registered with NCT02713555.
Copyright © 2022 Katrine Brodersen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Increased Insulin Secretion and Glucose Effectiveness in Obese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes following Bariatric Surgery.J Diabetes Res. 2023 Nov 14;2023:7127426. doi: 10.1155/2023/7127426. eCollection 2023. J Diabetes Res. 2023. PMID: 38020201 Free PMC article.
-
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Is More Effective than Sleeve Gastrectomy in Improving Postprandial Glycaemia and Lipaemia in Non-diabetic Morbidly Obese Patients: a Short-term Follow-up Analysis.Obes Surg. 2018 Dec;28(12):3997-4005. doi: 10.1007/s11695-018-3454-y. Obes Surg. 2018. PMID: 30112599
-
Effect of bariatric surgery on liver glucose metabolism in morbidly obese diabetic and non-diabetic patients.J Hepatol. 2014 Feb;60(2):377-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.09.012. Epub 2013 Sep 20. J Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 24060855 Clinical Trial.
-
Bariatric procedure selection in patients with type 2 diabetes: choice between Roux-en-Y gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy.Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2020 Feb;16(2):332-339. doi: 10.1016/j.soard.2019.11.013. Epub 2019 Dec 2. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2020. PMID: 31902579 Review.
-
Predictors of glycemic control after sleeve gastrectomy versus Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: A meta-analysis, meta-regression, and systematic review.Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2018 Dec;14(12):1822-1831. doi: 10.1016/j.soard.2018.08.027. Epub 2018 Sep 8. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2018. PMID: 30385071
Cited by
-
The Efficacy of Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass in Young-Onset Diabetes Mellitus: A Narrative Review.Cureus. 2024 Aug 23;16(8):e67562. doi: 10.7759/cureus.67562. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39310638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Potential Mechanism of Remission in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus After Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy.Obes Surg. 2024 Aug;34(8):3071-3083. doi: 10.1007/s11695-024-07378-z. Epub 2024 Jul 1. Obes Surg. 2024. PMID: 38951388 Review.
References
-
- Syn N. L., Cummings D. E., Wang L. Z., et al. Association of metabolic-bariatric surgery with long-term survival in adults with and without diabetes: a one-stage meta-analysis of matched cohort and prospective controlled studies with 174 772 participants. Lancet . 2021;397(10287):1830–1841. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00591-2. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

