Current Studies on Molecular Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance
- PMID: 36589630
- PMCID: PMC9803571
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/1863429
Current Studies on Molecular Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance
Abstract
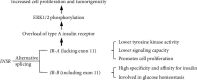
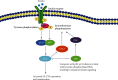
Diabetes is a metabolic disease that raises the risk of microvascular and neurological disorders. Insensitivity to insulin is a characteristic of type II diabetes, which accounts for 85-90 percent of all diabetic patients. The fundamental molecular factor of insulin resistance may be impaired cell signal transduction mediated by the insulin receptor (IR). Several cell-signaling proteins, including IR, insulin receptor substrate (IRS), and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), have been recognized as being important in the impaired insulin signaling pathway since they are associated with a large number of proteins that are strictly regulated and interact with other signaling pathways. Many studies have found a correlation between IR alternative splicing, IRS gene polymorphism, the complicated regulatory function of IRS serine/threonine phosphorylation, and the negative regulatory role of p85 in insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus. This review brings up-to-date knowledge of the roles of signaling proteins in insulin resistance in order to aid in the discovery of prospective targets for insulin resistance treatment.
Copyright © 2022 Jinli Pei et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that there is no conflict of interest that could compromise the review's objectivity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of streptozocin diabetes and diabetes treatment by islet transplantation on in vivo insulin signaling in rat heart.Diabetes. 2001 Dec;50(12):2709-20. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.50.12.2709. Diabetes. 2001. PMID: 11723053
-
A phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mTOR pathway mediates and PTEN antagonizes tumor necrosis factor inhibition of insulin signaling through insulin receptor substrate-1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Apr 10;98(8):4640-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.051042298. Epub 2001 Apr 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11287630 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of IRS-2 tyrosine phosphorylation in fasting and diabetes.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2001 Oct 25;183(1-2):63-9. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(01)00597-4. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2001. PMID: 11604226
-
Regulation of insulin resistance and glucose metabolism by interaction of PIM kinases and insulin receptor substrates.Arch Physiol Biochem. 2020 May;126(2):129-138. doi: 10.1080/13813455.2018.1498903. Epub 2018 Sep 29. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2020. PMID: 30270668 Review.
-
Research progress on drugs for diabetes based on insulin receptor/insulin receptor substrate.Biochem Pharmacol. 2023 Nov;217:115830. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115830. Epub 2023 Sep 23. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37748666 Review.
Cited by
-
In Silico Investigation of AKT2 Gene and Protein Abnormalities Reveals Potential Association with Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Sep 12;45(9):7449-7475. doi: 10.3390/cimb45090471. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37754255 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the Insulin-Heart Axis: Current Therapies and Future Directions.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 22;25(18):10173. doi: 10.3390/ijms251810173. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-hyperglycemic effects of Cissus quadrangularis extract via regulation of gluconeogenesis in type 2 diabetic db/db mice.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 10;15:1415670. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1415670. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39050759 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular dissection of the role of ACE2 in glucose homeostasis.Physiol Rev. 2025 Jul 1;105(3):935-973. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00027.2024. Epub 2025 Feb 7. Physiol Rev. 2025. PMID: 39918873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic Inflammation and Glycemic Control: Exploring the Bidirectional Link Between Periodontitis and Diabetes.Dent J (Basel). 2025 Feb 26;13(3):100. doi: 10.3390/dj13030100. Dent J (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40136728 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ribbing J., Hamrén B., Svensson M. K., Karlsson M. O. A model for glucose, insulin, and beta-cell dynamics in subjects with insulin resistance and patients with type 2 diabetes. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology . 2010;50(8):861–872. - PubMed
-
- Wang H., Gou W., Su C., et al. Association of gut microbiota with glycaemic traits and incident type 2 diabetes, and modulation by habitual diet: a population-based longitudinal cohort study in Chinese adults. Diabetologia . 2022;65(7):1145–1156. doi: 10.1007/s00125-022-05687-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical