Insulin-like growth factor-1 stimulates retinal cell proliferation via activation of multiple signaling pathways
- PMID: 36589675
- PMCID: PMC9800307
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crneur.2022.100068
Insulin-like growth factor-1 stimulates retinal cell proliferation via activation of multiple signaling pathways
Abstract
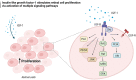
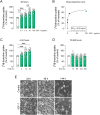
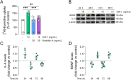
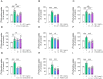
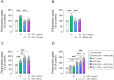
Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) plays critical roles in the development of the central nervous system (CNS), including the retina, regulating cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival. Here, we investigated the role of IGF-1 on retinal cell proliferation using primary cultures from rat neural retina. Our data show that IGF-1 stimulates retinal cell proliferation and regulates the expression of neurotrophic factors, such as interleukin-4 and brain-derived neurotrophic factor. In addition, our results indicates that IGF-1-induced retinal cell proliferation requires activation of multiple signaling pathways, including phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, protein kinase Src, phospholipase-C, protein kinase C delta, and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. We further show that activation of matrix metalloproteinases and epidermal growth factor receptor is also necessary for IGF-1 enhancing retinal cell proliferation. Overall, these results unveil potential mechanisms by which IGF-1 ensures retinal cell proliferation and support the notion that manipulation of IGF-1 signaling may be beneficial in CNS disorders associated with abnormal cell proliferation.
Keywords: Cell proliferation; Central nervous system; Epidermal growth factor; Insulin-like growth factor-1; Retina; Signaling pathway.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Braga L.E.G., Granja M.G., da Silva G.M., Giestal-de-Araujo E., dos Santos A.A. PMA increases M3 muscarinic receptor levels and decreases retinal cells proliferation through a change in the levels of cell-cycle regulatory proteins. Neurosci. Lett. 2013;550:29–34. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2013.06.045. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Braga L.E.G., Miranda R.L., Granja M.G., Giestal-de-Araujo E., Dos Santos A.A. PKC delta activation increases neonatal rat retinal cells survival in vitro: involvement of neurotrophins and M1 muscarinic receptors. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018;500(4):917–923. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.04.193. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

