XPO1-Mediated EIF1AX Cytoplasmic Relocation Promotes Tumor Migration and Invasion in Endometrial Carcinoma
- PMID: 36589683
- PMCID: PMC9800903
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/1361135
XPO1-Mediated EIF1AX Cytoplasmic Relocation Promotes Tumor Migration and Invasion in Endometrial Carcinoma
Abstract
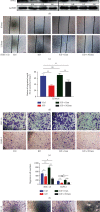
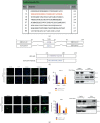
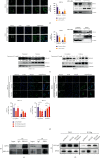
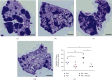
Dysregulation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 1A, X-linked (EIF1AX), has been implicated in the pathogenesis of some cancers. However, the role of EIF1AX in endometrial carcinoma (EC) remains unknown. We investigated the EIF1AX expression in EC patients and assessed its tumorigenesis-associated function and nucleocytoplasmic transport mechanism in vitro and in vivo. The results indicated that the cytoplasmic EIF1AX expression showed a gradual increase when going from endometrium normal tissue, simple endometrial hyperplasia, complex endometrial hyperplasia, and endometrial atypical hyperplasia to EC, while vice versa for the nuclear EIF1AX expression. In addition, the cytoplasmic EIF1AX expression was positively correlated with histologic type, high International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) grade, advanced FIGO stage, deeper infiltration, high Ki67 index, and shorter recurrence-free survival in EC patients. In vitro, short hairpin RNA-mediated EIF1AX depletion or SV40NLS-mediated EIF1AX import into the nucleus in multiple human EC cells potently suppressed cell migration and invasion, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and lung metastasis. Moreover, exportin 1 induced the transport of EIF1AX from the nucleus to the cytoplasm that could be inhibited by leptomycin B treatment or the mutation in the EIF1AX location sequence. These results demonstrate that cytoplasmic EIF1AX may play a key role in the incidence and promotion of EC, and thus, targeting EIF1AX or its nucleocytoplasmic transport process may offer an effective new therapeutic approach to EC.
Copyright © 2022 Yuhong Ye et al.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have any conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Long noncoding RNA EIF1AX-AS1 promotes endometrial cancer cell apoptosis by affecting EIF1AX mRNA stabilization.Cancer Sci. 2022 Apr;113(4):1277-1291. doi: 10.1111/cas.15275. Epub 2022 Feb 7. Cancer Sci. 2022. PMID: 35080085 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing of Cathepsin B suppresses the proliferation and invasion of endometrial cancer.Oncol Rep. 2013 Aug;30(2):723-30. doi: 10.3892/or.2013.2496. Epub 2013 May 27. Oncol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23708264
-
CEBPB promotes transformation of endometrial complex atypical hyperplasia to endometrial cancer.BMC Cancer. 2025 Jun 3;25(1):989. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14394-4. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40461968 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of astrocyte elevated gene-1: a novel marker of the pathogenesis, progression, and poor prognosis for endometrial cancer.Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2010 Oct;20(7):1188-96. doi: 10.1111/igc.0b013e3181ef8e21. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2010. PMID: 21495225
-
Nuclear expression of β-catenin in endometrial hyperplasia as marker of premalignancy.APMIS. 2019 Nov;127(11):699-709. doi: 10.1111/apm.12988. Epub 2019 Sep 11. APMIS. 2019. PMID: 31403731
Cited by
-
The function of PCSK9 in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity and its underlying mechanism.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):22067. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-03419-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40593844 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring ferroptosis and miRNAs: implications for cancer modulation and therapy.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Jun;480(6):3455-3476. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-05169-9. Epub 2025 Jan 27. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 39869280 Review.
-
Effects of MMP2 and its inhibitor TIMP2 on DNA damage, apoptosis and senescence of human lens epithelial cells induced by oxidative stress.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2024 Dec;56(6):619-630. doi: 10.1007/s10863-024-10044-9. Epub 2024 Nov 14. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2024. PMID: 39538054
-
Pharmacological modes of plant-derived compounds for targeting inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis: A comprehensive review on immunomodulatory perspective.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Apr;33(4):1537-1581. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01664-7. Epub 2025 Mar 13. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40074996 Review.
-
Impact of Organochlorine Pesticides Exposure on Histone Modification H3K9ac: Implications for Unexplained Recurrent Miscarriage.Biochem Genet. 2024 Aug 22. doi: 10.1007/s10528-024-10904-4. Online ahead of print. Biochem Genet. 2024. PMID: 39172205
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

