Detection of ROS1 gene fusions using next-generation sequencing for patients with malignancy in China
- PMID: 36589752
- PMCID: PMC9798300
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1035033
Detection of ROS1 gene fusions using next-generation sequencing for patients with malignancy in China
Abstract
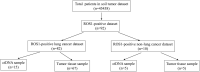
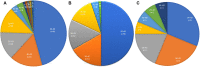
Objective: This study aimed to identify ROS1 fusion partners in Chinese patients with solid tumors. Methods: Next-generation sequencing (NGS) analysis was used to detect ROS1 rearrangement in 45,438 Chinese patients with solid tumors between 2015 and 2020, and the clinical characteristics and genetic features of gene fusion were evaluated. H&E staining of the excised tumor tissues was conducted. Samples with a tumor cell content ≥ 20% were included for subsequent DNA extraction and sequencing analysis. Results: A total of 92 patients with ROS1 rearrangements were identified using next-generation sequencing, and the most common histological type lung cancer. From the 92 ROS1 fusion cases, 24 ROS1 fusion partners had been identified, including 14 novel partners and 10 reported partners. Of these, CD74, EZR, SDC4, and TPM3 were the four most frequently occurring partners. Fourteen novel ROS1 fusion partners were detected in 16 patients, including DCBLD1-ROS1, FRK-ROS1, and VGLL2-ROS1. In many patients, the ROS1 breakpoint was located between exons 32 and 34. Conclusion: This study describes 14 novel ROS1 fusion partners based on the largest ROS1 fusion cohort, and the ROS1 breakpoint was mostly located between exons 32 and 34. Additionally, next-generation sequencing is an optional method for identifying novel ROS1 fusions.
Keywords: ROS1 breakpoint; ROS1 fusions partners; lung cancer; next-generation sequencing; solid tumor.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Chen, Huang, Zhang, Hu, Jiao and Quan.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors DZ and MH were employed by the company 3D Medicines Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CD74/SLC34A2-ROS1 Fusion Variants Involving the Transmembrane Region Predict Poor Response to Crizotinib in NSCLC Independent of TP53 Mutations.J Thorac Oncol. 2024 Apr;19(4):613-625. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2023.12.009. Epub 2023 Dec 7. J Thorac Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38070598
-
Potential Unreliability of Uncommon ALK, ROS1, and RET Genomic Breakpoints in Predicting the Efficacy of Targeted Therapy in NSCLC.J Thorac Oncol. 2021 Mar;16(3):404-418. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2020.10.156. Epub 2020 Nov 26. J Thorac Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33248323
-
Molecular and clinicopathological characteristics of ROS1-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancers identified by next-generation sequencing.Mol Oncol. 2020 Nov;14(11):2787-2795. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12789. Epub 2020 Sep 14. Mol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32871626 Free PMC article.
-
A Catalog of 5' Fusion Partners in ROS1-Positive NSCLC Circa 2020.JTO Clin Res Rep. 2020 Apr 28;1(3):100048. doi: 10.1016/j.jtocrr.2020.100048. eCollection 2020 Sep. JTO Clin Res Rep. 2020. PMID: 34589944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ROS1 protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of ROS1 fusion protein-driven non-small cell lung cancers.Pharmacol Res. 2017 Jul;121:202-212. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2017.04.022. Epub 2017 Apr 30. Pharmacol Res. 2017. PMID: 28465216 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of tropomyosin 3 in the development of malignant tumors.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 2;10(15):e35723. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35723. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39170461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Whole exome sequencing of well-differentiated liposarcoma and dedifferentiated liposarcoma in older woman: a case report.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Aug 15;10:1237246. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1237246. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37649981 Free PMC article.
-
Case Report: A case of first-line treatment for rare ROS1 fusion mutation lung adenocarcinoma with entrectinib.Front Oncol. 2025 Apr 16;15:1566687. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1566687. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40308505 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of CD74 Occurrence in Oncogenic Fusion Proteins.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 5;24(21):15981. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115981. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[A Case Report of Coexistence of EGFR and ROS-1 Gene Mutations in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2025 Jun 20;28(6):482-486. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2025.102.26. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40640100 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Anjum R., Zhang S., Squillace R., Clackson T., Garner A. P., Rivera V. M. (2012). 164 the dual ALK/EGFR inhibitor AP26113 also potently inhibits. Eur. J. Cancer 48, 50. 10.1016/s0959-8049(12)71962-7 - DOI
-
- Birch A. H., Arcand S. L., Oros K. K., Rahimi K., Watters A. K., Provencher D., et al. (2011). Chromosome 3 anomalies investigated by genome wide SNP analysis of benign, low malignant potential and low grade ovarian serous tumours. PloS one 6 (12), e28250. 10.1371/journal.pone.0028250 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

