In Vivo Cellular Magnetic Imaging: Labeled vs. Unlabeled Cells
- PMID: 36589903
- PMCID: PMC9798832
- DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202207626
In Vivo Cellular Magnetic Imaging: Labeled vs. Unlabeled Cells
Abstract
Superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO)-labeling of cells has been applied for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) cell tracking for over 30 years, having resulted in a dozen or so clinical trials. SPIO nanoparticles are biodegradable and can be broken down into elemental iron, and hence the tolerance of cells to magnetic labeling has been overall high. Over the years, however, single reports have accumulated demonstrating that the proliferation, migration, adhesion and differentiation of magnetically labeled cells may differ from unlabeled cells, with inhibition of chondrocytic differentiation of labeled human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) as a notable example. This historical perspective provides an overview of some of the drawbacks that can be encountered with magnetic labeling. Now that magnetic particle imaging (MPI) cell tracking is emerging as a new in vivo cellular imaging modality, there has been a renaissance in the formulation of SPIO nanoparticles this time optimized for MPI. Lessons learned from the occasional past pitfalls encountered with SPIO-labeling of cells for MRI may expedite possible future clinical translation of (combined) MRI/MPI cell tracking.
Keywords: Magnetic resonance imaging; cell tracking; immune cells; magnetic particle imaging; stem cells; superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement J.W.M.B. is a paid consultant to NovaDip Biosciences SA and SuperBranche. These arrangements have been reviewed and approved by the Johns Hopkins University in accordance with its conflict-of-interest policies. C.W. and A.S-Z. have nothing to disclose.
Figures


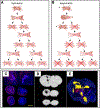
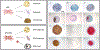
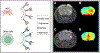
References
-
- Rosenberg SA, Lotze MT, Muul LM, Chang AE, Avis FP, Leitman S, Linehan WM, Robertson CN, Lee RE, Rubin JT, et al. , N Engl J Med 1987, 316, 889. - PubMed
-
- Rosenberg SA, Packard BS, Aebersold PM, Solomon D, Topalian SL, Toy ST, Simon P, Lotze MT, Yang JC, Seipp CA, et al. , N Engl J Med 1988, 319, 1676. - PubMed
-
- Anguille S, Smits EL, Lion E, van Tendeloo VF, Berneman ZN, The Lancet Oncology 2014, 15, e257. - PubMed
-
- Gill S, Maus MV, Porter DL, Blood Rev 2016, 30, 157. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
