A visual detection strategy for SARS-CoV-2 based on dual targets-triggering DNA walker
- PMID: 36590306
- PMCID: PMC9792190
- DOI: 10.1016/j.snb.2022.133252
A visual detection strategy for SARS-CoV-2 based on dual targets-triggering DNA walker
Abstract
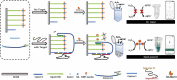
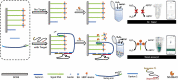
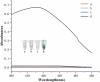
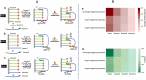
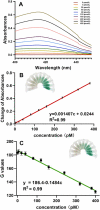
SARS-CoV-2, a highly transmissible and mutagenic virus, made huge threats to global public health. The detection strategies, which are free from testing site requirements, and the reagents and instruments are portable, are vital for early screening and play a significant role in curbing the spread. This work proposed a silver-coated glass slide (SCGS)/DNA walker based on a dual targets-triggering mechanism, enzyme-catalyzed amplification, and smartphone data analysis, which build a portable visual detection strategy for the SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) gene. By this method, the detection was reflected by the ultraviolet absorbance changes and visible color changes to the naked eye which was analyzed by Red-Green-Blue (RGB) data analysis via smartphone within 30 min, simplifying the detection process and shortening the detection time. Meanwhile, the dual targets-triggering mechanism and dual signal amplification strategy ensured detection specificity and sensitivity. Further, the practicability was verified by the detection of the real sample which provided this method an application potential in SARS-CoV-2 rapid detection.
Keywords: Biosensor; DNA Walker; SARS-CoV-2; Silver coated glass slide.
© 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rational engineering the DNA tetrahedrons of dual wavelength ratiometric electrochemiluminescence biosensor for high efficient detection of SARS-CoV-2 RdRp gene by using entropy-driven and bipedal DNA walker amplification strategy.Chem Eng J. 2022 Jan 1;427:131686. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.131686. Epub 2021 Aug 9. Chem Eng J. 2022. PMID: 34400874 Free PMC article.
-
Rational Engineering of the DNA Walker Amplification Strategy by Using a Au@Ti3C2@PEI-Ru(dcbpy)32+ Nanocomposite Biosensor for Detection of the SARS-CoV-2 RdRp Gene.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021 May 5;13(17):19816-19824. doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c04453. Epub 2021 Apr 23. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021. PMID: 33890471
-
A strategy combining 3D-DNA Walker and CRISPR-Cas12a trans-cleavage activity applied to MXene based electrochemiluminescent sensor for SARS-CoV-2 RdRp gene detection.Talanta. 2022 Jan 1;236:122868. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122868. Epub 2021 Sep 10. Talanta. 2022. PMID: 34635250 Free PMC article.
-
A smartphone-based platform for ratiometric visualization of SARS-CoV-2 via an oligonucleotide probe.Mikrochim Acta. 2022 Jul 4;189(8):268. doi: 10.1007/s00604-022-05364-9. Mikrochim Acta. 2022. PMID: 35781842
-
A DNA framework-based dual signal amplification biosensor for portable detection of SARS-CoV-2 and its mutations.Chem Commun (Camb). 2023 Jul 13;59(57):8838-8841. doi: 10.1039/d3cc02526h. Chem Commun (Camb). 2023. PMID: 37366142
Cited by
-
Machine learning for optical chemical multi-analyte imaging : Why we should dare and why it's not without risks.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2023 Jun;415(14):2749-2761. doi: 10.1007/s00216-023-04678-8. Epub 2023 Apr 18. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2023. PMID: 37071140 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Based on Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests (NAATs) and Its Integration into Nanomedicine and Microfluidic Devices as Point-of-Care Testing (POCT).Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 16;24(12):10233. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210233. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373381 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
-
WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard, (n.d.). https://covid19.who.int. (Accessed 11 September 2022).
-
-
- Shi R., Shan C., Duan X., Chen Z., Liu P., Song J., Song T., Bi X., Han C., Wu L., Gao G., Hu X., Zhang Y., Tong Z., Huang W., Liu W.J., Wu G., Zhang B., Wang L., Qi J., Feng H., Wang F.-S., Wang Q., Gao G.F., Yuan Z., Yan J. A human neutralizing antibody targets the receptor-binding site of SARS-CoV-2. Nature. 2020;584:120–124. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2381-y. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kim C., Ryu D.-K., Lee J., Kim Y.-I., Seo J.-M., Kim Y.-G., Jeong J.-H., Kim M., Kim J.-I., Kim P., Bae J.S., Shim E.Y., Lee M.S., Kim M.S., Noh H., Park G.-S., Park J.S., Son D., An Y., Lee J.N., Kwon K.-S., Lee J.-Y., Lee H., Yang J.-S., Kim K.-C., Kim S.S., Woo H.-M., Kim J.-W., Park M.-S., Yu K.-M., Kim S.-M., Kim E.-H., Park S.-J., Jeong S.T., Yu C.H., Song Y., Gu S.H., Oh H., Koo B.-S., Hong J.J., Ryu C.-M., Park W.B., Oh M.-D., Choi Y.K., Lee S.-Y. A therapeutic neutralizing antibody targeting receptor binding domain of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Nat. Commun. 2021;12:288. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20602-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

