PROSE: Prospective Randomized Trial of the On-X Mechanical Prosthesis and the St Jude Medical Mechanical Prosthesis Evaluation: Part 2: Study results-prostheses, positions, and economic development
- PMID: 36590733
- PMCID: PMC9801238
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xjon.2022.07.011
PROSE: Prospective Randomized Trial of the On-X Mechanical Prosthesis and the St Jude Medical Mechanical Prosthesis Evaluation: Part 2: Study results-prostheses, positions, and economic development
Abstract
Objectives: The Prospective Randomized On-X Mechanical Prosthesis Versus St Jude Medical Mechanical Prosthesis Evaluation (PROSE) trial purpose was to investigate whether a current-generation mechanical prosthesis (On-X; On-X Life Technologies/Artivion Inc) reduced the incidence of thromboembolic-related complications compared with a previous-generation mechanical prosthesis (St Jude Medical Mechanical Prosthesis; Abbott/St Jude Medical). This second report documents the valve-related complications by individual prostheses and by Western and Developing populations.
Methods: The PROSE trial study was conducted in 28 worldwide centers and incorporated 855 subjects randomized between 2003 and 2016. The study enrollment was discontinued on August 31, 2016. The study protocol, and analyses of 10 demographic variables and 24 risk factors were published in detail in 2021.
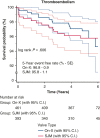
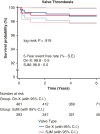
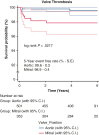
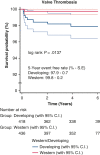
Results: The total patient population (N = 855) included patients receiving an On-X valve (n = 462) and a St Jude Medical valve (n = 393). The overall freedom evaluation showed no differences at 5 years between the prostheses for thromboembolism or for valve thrombosis. There were also no differences in mortality. There were several differences between Developing and Western populations. The freedom relations at 5 years for mortality favored Western over Developing populations. Valve thrombosis was differentiated by position and site: aortic < mitral (P = .007) and Western < Developing (P = .005). In the mitral position there were no cases in Western populations, whereas there were 8 in Developing populations (P = .217).
Conclusions: The On-X valve and St Jude Medical valve performed equally well in the study with no differences found. The only differentiation occurred with valve thrombosis in the mitral position more than the aortic position and occurring in Developing more than Western populations. The occurrence of valve thrombosis was also related to a younger population possibly due to anticoagulation compliance based on record review.
Keywords: BMI, body mass index; CHF, congestive heart failure; INR, international normalized ratio; NYHA, New York Heart Association; PROSE, Prospective Randomized On-X Mechanical Prosthesis Versus St Jude Medical Mechanical Prosthesis Evaluation; TE, thromboembolism; VT, valve thrombosis; economic development; position; prosthesis.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Figures







References
-
- Jamieson W.R.E., Ely J.L., Brink J., Pennel T., Bannon P., Patel J., et al. PROSE: Prospective Randomized Trial of the On-X Mechanical Prosthesis and the St Jude Medical Mechanical Prosthesis Evaluation: part 1(patient dynamics): preoperative demographics and preoperative and operative risk factors. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2021;16:323–334. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akins C.W., Miller D.C., Turina M.I., Kouchoukos N.T., Blackstone E.H., Grunkemeier G.L., et al. Guidelines for reporting mortality and morbidity after cardiac valve interventions. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2008;135:732–738. - PubMed
-
- US Food and Drug Administration On-X valve summary of safety and effectiveness. PMA P000037, May 30, 2001, and PMA P000037 S002. March 6, 2002. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/pdf/P000037S001b.pdf
-
- Palatianos G.M., Laczkovics A.M., Simon P., Pomar J.L., Birnbaum D.E., Greve H.H., et al. Multicentered European study on safety and effectiveness on the On-X prosthetic heart valve: intermediate follow-up. Ann Thorac Surg. 2007;83:40–46. - PubMed
-
- McNicholas K.W., Ivey T.D., Metras J., Szentpetery S., Marra S.W., Masters R.G., et al. North American multicenter experience with the On-X prosthetic heart valve. J Heart Valve Dis. 2006;15:73–79. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

