Ameliorative effect of biosynthesized titanium dioxide nanoparticles using garlic extract on the body weight and developmental toxicity of liver in albino rats compared with chemically synthesized nanoparticles
- PMID: 36590803
- PMCID: PMC9800981
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2022.1049817
Ameliorative effect of biosynthesized titanium dioxide nanoparticles using garlic extract on the body weight and developmental toxicity of liver in albino rats compared with chemically synthesized nanoparticles
Abstract
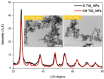
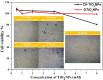
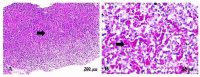
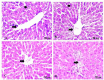
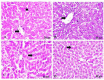
The application of metallic nanoparticles poses risks to human and animal health. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2NPs) are the most commonly synthesized metallic oxides in the world. Exposure to TiO2NPs can cause toxicity in the target organisms. This study aimed to evaluate the effects of green and chemical TiO2NPs on maternal and embryo-fetal livers. Green TiO2NPs using garlic extract (GTiO2NPs) and chemical TiO2NPs (CHTiO2NPs) were synthesized and characterized by x-ray powder diffraction and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy. The cytotoxicity of both chemical and green TiO2NPs was determined against HepG2 cell lines. Fifty pregnant female Albino rats were equally and randomly divided into five groups. Group 1 was kept as a control. Groups 2 and 3 were orally treated with 100 and 300 mg/kg body weight of CHTiO2NPs, respectively. Groups 4 and 5 were orally treated with 100 and 300 mg/kg of GTiO2NPs, respectively, from day 6 to 19 of gestation. All dams were euthanized on gestation day 20. All live fetuses were weighed and euthanized. Blood and tissue samples were collected for biochemical, histopathological, and Bax-immunohistochemical expression analyses. Our results indicated that garlic could be used as a reducing agent for the synthesis of TiO2NPs, and the produced NPs have no toxic effect against HepG2 cells compared with CHTiO2NPs. The maternal and fetal bodyweights were greatly reduced among the chemically TiO2NPs induced animals. The mean serum level of AST and ALT activities and the total protein level significantly increased when TiO2NPs were administered at high doses. Histologically, the CHTiO2NPs-treated groups revealed vacuolated and necrotized hepatocytes with congested and dilated blood vessels in the fetal and maternal livers. The immunohistochemistry revealed distinct positive staining of Bax expressed in the hepatocytes. Nevertheless, the biosynthesis of TiO2NPs using garlic extract had a minimal effect on the normal architecture of the liver. It could be concluded that the bioactivity of TiO2NPs can be modified by green synthesis using garlic extract. Compared to the CHTiO2NPs, the exposure to GTiO2NPs showed reduced liver damage in maternal and embryo-fetal rats.
Keywords: Bax-immunohistochemically; TiO2NPs; bodyweight; fetuses; garlic; histology; liver.
Copyright © 2022 Kamal, Ebnalwaled, Al-Amgad, Said, Metwally, Zigo, Ondrašovičová and Rehan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The Nephroprotective Effect of In Utero Administration of Green Synthesized Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles in Albino Rats.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2024 Aug;202(8):3686-3700. doi: 10.1007/s12011-023-03940-5. Epub 2023 Nov 16. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2024. PMID: 37968492
-
Genetic effects of chemically and biosynthesized titanium dioxide nanoparticles in vitro and in vivo of female rats and their fetuses.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Aug 8;10:1142305. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1142305. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37614463 Free PMC article.
-
Duration-dependent effects induced by titanium dioxide nanoparticles on pancreas of adult male albino rats (histological and biochemical study).Ultrastruct Pathol. 2020 Nov 20;44(4-6):342-358. doi: 10.1080/01913123.2020.1786203. Epub 2020 Jun 30. Ultrastruct Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32600082
-
Green synthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles using plant biomass and their applications- A review.Chemosphere. 2022 Aug;300:134612. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134612. Epub 2022 Apr 14. Chemosphere. 2022. PMID: 35430203 Review.
-
Physical, chemical, and biological routes of synthetic titanium dioxide nanoparticles and their crucial role in temperature stress tolerance in plants.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 16;10(4):e26537. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26537. eCollection 2024 Feb 29. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38420474 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of the bioactivity of bioinspired magnesium oxide nanoparticles from the Azadirachta indica extract.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Nov 29;12:1480694. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1480694. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39677838 Free PMC article.
-
Biogenic Zinc oxide nanoparticles from Celosia argentea: toward improved antioxidant, antibacterial, and anticancer activities.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Dec 15;11:1283898. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1283898. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 38162186 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative approaches to antibiotics in the control of mastitis in dairy cows: a review.Vet Res Commun. 2025 Mar 24;49(3):150. doi: 10.1007/s11259-025-10720-0. Vet Res Commun. 2025. PMID: 40126814 Review.
-
The Nephroprotective Effect of In Utero Administration of Green Synthesized Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles in Albino Rats.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2024 Aug;202(8):3686-3700. doi: 10.1007/s12011-023-03940-5. Epub 2023 Nov 16. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2024. PMID: 37968492
-
Genetic effects of chemically and biosynthesized titanium dioxide nanoparticles in vitro and in vivo of female rats and their fetuses.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Aug 8;10:1142305. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1142305. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37614463 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

