Case report: Successful treatment of non-bullous lichen planus pemphigoides with dupilumab
- PMID: 36590953
- PMCID: PMC9800862
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1023458
Case report: Successful treatment of non-bullous lichen planus pemphigoides with dupilumab
Abstract
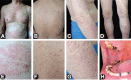
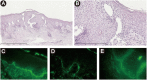
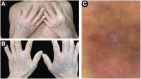
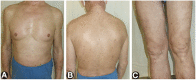
Lichen planus pemphigoides (LPP) is a rare autoimmune bullous disease, characterized by the coexistence of lichen planus and subepidermal bullae. However, the minority of LPP patients present with papules rather than vesicles or blisters, which is defined as non-bullous LPP. The diagnosis of LPP relies on manifestations, histopathology, serological assay, and direct immunofluorescence of linear disposition of IgG and/or C3 at the basement membrane zone. Up to now, no standard therapeutic strategies have been proposed for the treatment of LPP. Herein, we describe an uncommon non-bullous LPP patient with widespread papules and erythema, probably induced by vaccination. During hospitalization, he had a poor response to the conventional treatment of topical and systemic corticosteroids, and his condition was finally alleviated by the addition of dupilumab. For LPP patients with a traditional medication failure, or who were not suitable for a higher dose of corticosteroids, a combination with dupilumab could be an alternative option.
Keywords: corticosteroid; dupilumab; lichen planus; lichen planus pemphigoids; non-bullous; vaccine.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Xie, Wang, Fang, Jin and Zuo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

