Association between lactate-to-albumin ratio and 28-days all-cause mortality in patients with acute pancreatitis: A retrospective analysis of the MIMIC-IV database
- PMID: 36591285
- PMCID: PMC9795001
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1076121
Association between lactate-to-albumin ratio and 28-days all-cause mortality in patients with acute pancreatitis: A retrospective analysis of the MIMIC-IV database
Abstract
Objective: The Lactate-to-Albumin Ratio (LAR) has been applied as a new predictor in sepsis, heart failure, and acute respiratory failure. However, the role of LAR in predicting all-cause mortality in patients with acute pancreatitis has not been evaluated. Therefore, this study aimed to elucidate the correlation between LAR and 28-d all-cause mortality in patients with Acute Pancreatitis (AP).
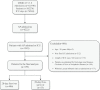
Methods: This study is a retrospective cohort study with the data from the MIMIC-IV (v1.0) database. We included adult patients with acute pancreatitis who were admitted to the intensive care unit in the study. The primary outcome was to evaluate the ability of LAR to predict death at 28-d of hospital admission in patients with AP.
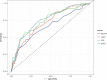
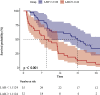
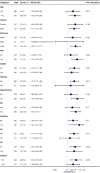
Results: A total of 539 patients with acute pancreatitis were included in this study. They were divided into a survival group (486 patients) and a death group (53 patients) according to whether they survived within 28-d of admission, and the mortality rate of patients within 28-d of admission was 9.8%. LAR was shown to be an independent predictor of all-cause mortality within 28-d of admission in patients with AP by multivariate COX regression analysis (HR, 1.59; 95% CI, 1.23 - 2.05; P < 0.001). the Area Under the Curve (AUC) value for LAR was 74.26% (95% CI: 67.02% - 81.50%), which was higher than that for arterial blood lactate (AUC = 71.25%) and serum albumin (AUC = 65.92%) alone. It was not inferior even when compared to SOFA (AUC = 75.15%). The optimal cutoff value for separating the survival and death groups according to Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) was found to be 1.1124. plotting Kaplan-Meier analysis with this cutoff value showed that patients with LAR ≥ 1.1124 had significantly higher all-cause mortality within 28-d of admission than those with LAR < 1.1124 (P < 0.001). The final subgroup analysis showed no significant interaction of LAR with each subgroup (P for interaction: 0.06 - 0.974).
Conclusion: LAR can be used as an independent predictor of all-cause mortality in AP patients within 28-d of admission, with superior prognostic performance than arterial blood lactate or serum albumin alone.
Keywords: 28-days; acute pancreatitis; all-cause mortality; cohort; lactate/albumin ratio; prognosis.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Zheng, Wu, Wang, Yan, Wang, Yu and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

