Severe toxic rhabdomyolysis under combined palbociclib and simvastatin treatment: A case report
- PMID: 36591506
- PMCID: PMC9795206
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1026434
Severe toxic rhabdomyolysis under combined palbociclib and simvastatin treatment: A case report
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Severe toxic rhabdomyolysis under combined palbociclib and simvastatin treatment: A case report.Front Oncol. 2023 Feb 7;13:1149399. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1149399. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36824143 Free PMC article.
Abstract
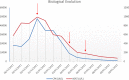
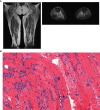
We report the fourth described case of severe toxic rhabdomyolysis occurring in an 81-year-old woman caused by the concomitant administration of palbociclib taken at the usual dosage (125 mg per day) and simvastatin. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first reported case successfully treated by plasma exchanges, with complete functional recovery within two months. The severity of this case justifies further consideration of pharmacokinetic interactions between palbociclib or other CDK-4-6 inhibitors and statins, which potentially increase the risk of an adverse event.
Keywords: interaction; myositis; palbociclib; plasmatic exchange; rhabdomyolysis; simvastatin.
Copyright © 2022 François, Anna, Jérémie, Quentin, Olivier, Emmanuelle, Céline, Florence, Pierre and Anaïs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Parrish KE, Pokorny J, Mittapalli RK, Bakken K, Sarkaria JN, Elmquist WF. Efflux transporters at the blood-brain barrier limit delivery and efficacy of cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor palbociclib (PD-0332991) in an orthotopic brain tumor model. J Pharmacol Exp Ther (2015) 355:264–71. doi: 10.1124/jpet.115.228213 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gopalan P, Pinder-Schenck M, Chiappori A, Ivey A, Villegas A, Kaye F. A phase II clinical trial of the CDK 4/6 inhibitor palbociclib (PD 0332991) in previously treated, advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with inactivated CDKN2A. J Clin Oncol (2014) 32:8077–7. doi: 10.1200/jco.2014.32.15_suppl.8077 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

