How to use biomarkers of infection or sepsis at the bedside: guide to clinicians
- PMID: 36592205
- PMCID: PMC9807102
- DOI: 10.1007/s00134-022-06956-y
How to use biomarkers of infection or sepsis at the bedside: guide to clinicians
Abstract
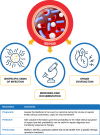
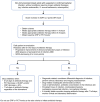
Sepsis is defined as a life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection. In this context, biomarkers could be considered as indicators of either infection or dysregulated host response or response to treatment and/or aid clinicians to prognosticate patient risk. More than 250 biomarkers have been identified and evaluated over the last few decades, but no biomarker accurately differentiates between sepsis and sepsis-like syndrome. Published data support the use of biomarkers for pathogen identification, clinical diagnosis, and optimization of antibiotic treatment. In this narrative review, we highlight how clinicians could improve the use of pathogen-specific and of the most used host-response biomarkers, procalcitonin and C-reactive protein, to improve the clinical care of patients with sepsis. Biomarker kinetics are more useful than single values in predicting sepsis, when making the diagnosis and assessing the response to antibiotic therapy. Finally, integrated biomarker-guided algorithms may hold promise to improve both the diagnosis and prognosis of sepsis. Herein, we provide current data on the clinical utility of pathogen-specific and host-response biomarkers, offer guidance on how to optimize their use, and propose the needs for future research.
Keywords: Antibiotic stewardship; Biomarkers; Diagnosis; Intensive care unit; Sepsis.
© 2022. Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
PP received fees for a lecture from Gilead, Pfizer and Mundipharma, consulting from MSD and Sanofi, and an unrestricted research grant from Abionic. AR received fess for lectures from MSD. ACM received fees for lectures from Boston Scientific and consulting from Cambridge Infection Diagnostics, is supported by a Clinician Scientist Fellowship from the Medical Research Council (MR/V006118/1). MS received fees for lectures at educational meetings for Biomerieux and Radiometer, consulting from Abbott, Biomerieux, deePull, Roche Diagnostics, Safeguard Biosystems and Spiden and performed preclinical and clinical research studies with Biomerieux, Cornel Scientific, DSTL (UK Ministry of Defence), Gentian. RF received fees for lectures, speakers’ bureaus or advisory boards from Grifols, MSD, Pfizer, Gilead, Shionogi, Thermofisher, Hill Rom, AOP Health and BD. LC, FD-P, AH, AK, VN, JS, PR, DS, GW, AT declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

