Extracellular vesicles from mesenchymal stem cells reduce neuroinflammation in hippocampus and restore cognitive function in hyperammonemic rats
- PMID: 36593485
- PMCID: PMC9806918
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-022-02688-4
Extracellular vesicles from mesenchymal stem cells reduce neuroinflammation in hippocampus and restore cognitive function in hyperammonemic rats
Abstract
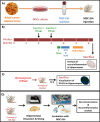
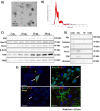
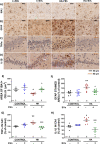
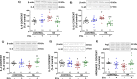
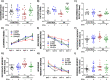
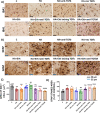
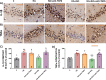
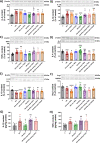
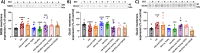
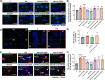
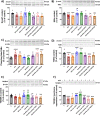
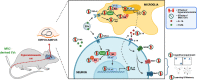
Chronic hyperammonemia, a main contributor to hepatic encephalopathy (HE), leads to neuroinflammation which alters neurotransmission leading to cognitive impairment. There are no specific treatments for the neurological alterations in HE. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) reduce neuroinflammation in some pathological conditions. The aims were to assess if treatment of hyperammonemic rats with EVs from MSCs restores cognitive function and analyze the underlying mechanisms. EVs injected in vivo reach the hippocampus and restore performance of hyperammonemic rats in object location, object recognition, short-term memory in the Y-maze and reference memory in the radial maze. Hyperammonemic rats show reduced TGFβ levels and membrane expression of TGFβ receptors in hippocampus. This leads to microglia activation and reduced Smad7-IkB pathway, which induces NF-κB nuclear translocation in neurons, increasing IL-1β which alters AMPA and NMDA receptors membrane expression, leading to cognitive impairment. These effects are reversed by TGFβ in the EVs from MSCs, which activates TGFβ receptors, reducing microglia activation and NF-κB nuclear translocation in neurons by normalizing the Smad7-IkB pathway. This normalizes IL-1β, AMPA and NMDA receptors membrane expression and, therefore, cognitive function. EVs from MSCs may be useful to improve cognitive function in patients with hyperammonemia and minimal HE.
Keywords: Cognitive impairment; Extracellular vesicles; Hyperammonemia; Mesenchymal stem cells; Neuroinflammation.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extracellular vesicles from mesenchymal stem cells improve neuroinflammation and neurotransmission in hippocampus and cognitive impairment in rats with mild liver damage and minimal hepatic encephalopathy.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024 Dec 18;15(1):472. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-04076-6. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 39696620 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles from hyperammonemic rats induce neuroinflammation in hippocampus and impair cognition in control rats.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023 Mar 15;80(4):90. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-04750-7. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 36922433 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo administration of extracellular cGMP normalizes TNF-α and membrane expression of AMPA receptors in hippocampus and spatial reference memory but not IL-1β, NMDA receptors in membrane and working memory in hyperammonemic rats.Brain Behav Immun. 2016 Oct;57:360-370. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2016.05.011. Epub 2016 May 14. Brain Behav Immun. 2016. PMID: 27189036
-
Pathological and therapeutic effects of extracellular vesicles in neurological and neurodegenerative diseases.Neural Regen Res. 2024 Jan;19(1):55-61. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.375301. Neural Regen Res. 2024. PMID: 37488844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peripheral inflammation induces neuroinflammation that alters neurotransmission and cognitive and motor function in hepatic encephalopathy: Underlying mechanisms and therapeutic implications.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2019 Jun;226(2):e13270. doi: 10.1111/apha.13270. Epub 2019 Mar 22. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2019. PMID: 30830722 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular and therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on autoimmune diseases.World J Stem Cells. 2025 Jul 26;17(7):107202. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i7.107202. World J Stem Cells. 2025. PMID: 40740529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanopathways modulating postoperative cognitive dysfunction: extracellular vesicles.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Jun 30;13:1613378. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1613378. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40661144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Purinergic Signaling in Autism Spectrum Disorder: Bridging the Gap between Cell-Based Strategies and Neuro-Immune Modulation.Biomedicines. 2024 Jun 13;12(6):1310. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12061310. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38927517 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles from Different Mesenchymal Stem Cell Types Exhibit Distinctive Surface Protein Profiling and Molecular Characteristics: A Comparative Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 4;26(7):3393. doi: 10.3390/ijms26073393. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40244251 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of the Common Neurodegenerative Disorders: Current Therapeutic Approaches and the Potential Role of Bioactive Peptides.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2024;25(7):507-526. doi: 10.2174/0113892037275221240327042353. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2024. PMID: 38561605 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- PROMETEOII/2018/051/Conselleria de Cultura, Educación y Ciencia, Generalitat Valenciana
- FPU17/01698/Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades
- PID2020-113388RB-I00/Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación
- CIPROM2021/082/Conselleria d'Educació, Investigació, Cultura i Esport
- CD17/00031/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

