A stapled chromogranin A-derived peptide homes in on tumors that express αvβ6 or αvβ8 integrins
- PMID: 36594095
- PMCID: PMC9760430
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.76148
A stapled chromogranin A-derived peptide homes in on tumors that express αvβ6 or αvβ8 integrins
Abstract
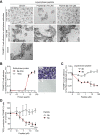
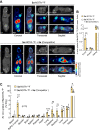
Rationale: The αvβ6- and αvβ8-integrins, two cell-adhesion receptors upregulated in many tumors and involved in the activation of the latency associated peptide (LAP)/TGFβ complex, represent potential targets for tumor imaging and therapy. We investigated the tumor-homing properties of a chromogranin A-derived peptide containing an RGDL motif followed by a chemically stapled alpha-helix (called "5a"), which selectively recognizes the LAP/TGFβ complex-binding site of αvβ6 and αvβ8. Methods: Peptide 5a was labeled with IRDye 800CW (a near-infrared fluorescent dye) or with 18F-NOTA (a label for positron emission tomography (PET)); the integrin-binding properties of free peptide and conjugates were then investigated using purified αvβ6/αvβ8 integrins and various αvβ6/αvβ8 single - or double-positive cancer cells; tumor-homing, biodistribution and imaging properties of the conjugates were investigated in subcutaneous and orthotopic αvβ6-positive carcinomas of the pancreas, and in mice bearing subcutaneous αvβ8-positive prostate tumors. Results: In vitro studies showed that 5a can bind both integrins with high affinity and inhibits cell-mediated TGFβ activation. The 5a-IRDye and 5a-NOTA conjugates could bind purified αvβ6/αvβ8 integrins with no loss of affinity compared to free peptide, and selectively recognized various αvβ6/αvβ8 single- or double-positive cancer cells, including cells from pancreatic carcinoma, melanoma, oral mucosa, bladder and prostate cancer. In vivo static and dynamic optical near-infrared and PET/CT imaging and biodistribution studies, performed in mice with subcutaneous and orthotopic αvβ6-positive carcinomas of the pancreas, showed high target-specific uptake of fluorescence- and radio-labeled peptide by tumors and low non-specific uptake in other organs and tissues, except for excretory organs. Significant target-specific uptake of fluorescence-labeled peptide was also observed in mice bearing αvβ8-positive prostate tumors. Conclusions: The results indicate that 5a can home to αvβ6- and/or αvβ8-positive tumors, suggesting that this peptide can be exploited as a ligand for delivering imaging or anticancer agents to αvβ6/αvβ8 single- or double-positive tumors, or as a tumor-homing inhibitor of these TGFβ activators.
Keywords: RGD motif; TGFβ; cancer.; chromogranin A; αvβ6 and αvβ8 integrins.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: AC, AG, and FC are inventors of a patent regarding CgA-derived peptides.
Figures


References
-
- Koivisto L, Bi J, Hakkinen L, Larjava H. Integrin alphavbeta6: Structure, function and role in health and disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2018;99:186–96. - PubMed
-
- Elayadi AN, Samli KN, Prudkin L, Liu YH, Bian A, Xie XJ. et al. A peptide selected by biopanning identifies the integrin alphavbeta6 as a prognostic biomarker for nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2007;67:5889–95. - PubMed
-
- Sipos B, Hahn D, Carceller A, Piulats J, Hedderich J, Kalthoff H. et al. Immunohistochemical screening for beta6-integrin subunit expression in adenocarcinomas using a novel monoclonal antibody reveals strong up-regulation in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas in vivo and in vitro. Histopathology. 2004;45:226–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

