Single-spoke binning: Reducing motion artifacts in abdominal radial stack-of-stars imaging
- PMID: 36594436
- PMCID: PMC11955222
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.29576
Single-spoke binning: Reducing motion artifacts in abdominal radial stack-of-stars imaging
Abstract
Purpose: To increase the effectiveness of respiratory gating in radial stack-of-stars MRI, particularly when imaging at high spatial resolutions or with multiple echoes.
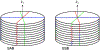
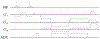
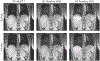
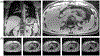
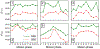
Methods: Free induction decay (FID) navigators were integrated into a three-dimensional gradient echo radial stack-of-stars pulse sequence. These navigators provided a motion signal with a high temporal resolution, which allowed single-spoke binning (SSB): each spoke at each phase encode step was sorted individually to the corresponding motion state of the respiratory signal. SSB was compared with spoke-angle binning (SAB), in which all phase encode steps of one projection angle were sorted without the use of additional navigator data. To illustrate the benefit of SSB over SAB, images of a motion phantom and of six free-breathing volunteers were reconstructed after motion-gating using either method. Image sharpness was quantitatively compared using image gradient entropies.
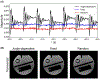
Results: The proposed method resulted in sharper images of the motion phantom and free-breathing volunteers. Differences in gradient entropy were statistically significant (p = 0.03) in favor of SSB. The increased accuracy of motion-gating led to a decrease of streaking artifacts in motion-gated four-dimensional reconstructions. To consistently estimate respiratory signals from the FID-navigator data, specific types of gradient spoiler waveforms were required.
Conclusion: SSB allowed high-resolution motion-corrected MR imaging, even when acquiring multiple gradient echo signals or large acquisition matrices, without sacrificing accuracy of motion-gating. SSB thus relieves restrictions on the choice of pulse sequence parameters, enabling the use of motion-gated radial stack-of-stars MRI in a broader domain of clinical applications.
Keywords: FID navigators; motion binning; motion correction; radial sampling; respiratory gating.
© 2023 The Authors. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures
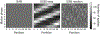


References
-
- Schultz CL, Alfidi RJ, Nelson AD, Kopiwoda SY, Clampitt ME. The effect of motion on two-dimensional Fourier transformation magnetic resonance images. Radiology. 1984;152:117–121. - PubMed
-
- Gomori JM, Horev G, Tamary H, et al. Hepatic iron overload: quantitative MR imaging. Radiology. 1991;179:367–369. - PubMed
-
- Harisinghani MG, Barentsz J, Hahn PF, et al. Noninvasive detection of clinically occult lymph-node metastases in prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:2491–2499. - PubMed
-
- Gouw DJJM, Maas MC, Slagt C, et al. Controlled mechanical ventilation to detect regional lymph node metastases in esophageal cancer using USPIO-enhanced MRI; comparison of image quality. Magn Reson Imaging. 2020;74:258–265. - PubMed
-
- Glover GH, Pauly JM. Projection reconstruction techniques for reduction of motion effects in MRI. Magn Reson Med. 1992;28:275–289. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

