Exploring the potential of OMOP common data model for process mining in healthcare
- PMID: 36595527
- PMCID: PMC9810199
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0279641
Exploring the potential of OMOP common data model for process mining in healthcare
Abstract
Background and objective: Recently, Electronic Health Records (EHR) are increasingly being converted to Common Data Models (CDMs), a database schema designed to provide standardized vocabularies to facilitate collaborative observational research. To date, however, rare attempts exist to leverage CDM data for healthcare process mining, a technique to derive process-related knowledge (e.g., process model) from event logs. This paper presents a method to extract, construct, and analyze event logs from the Observational Medical Outcomes Partnership (OMOP) CDM for process mining and demonstrates CDM-based healthcare process mining with several real-life study cases while answering frequently posed questions in process mining, in the CDM environment.
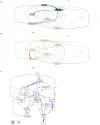
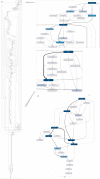
Methods: We propose a method to extract, construct, and analyze event logs from the OMOP CDM for process types including inpatient, outpatient, emergency room processes, and patient journey. Using the proposed method, we extract the retrospective data of several surgical procedure cases (i.e., Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy (TLH), Total Hip Replacement (THR), Coronary Bypass (CB), Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI), Pancreaticoduodenectomy (PD)) from the CDM of a Korean tertiary hospital. Patient data are extracted for each of the operations and analyzed using several process mining techniques.
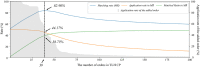
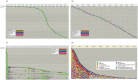
Results: Using process mining, the clinical pathways, outpatient process models, emergency room process models, and patient journeys are demonstrated using the extracted logs. The result shows CDM's usability as a novel and valuable data source for healthcare process analysis, yet with a few considerations. We found that CDM should be complemented by different internal and external data sources to address the administrative and operational aspects of healthcare processes, particularly for outpatient and ER process analyses.
Conclusion: To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to exploit CDM for healthcare process mining. Specifically, we provide a step-by-step guidance by demonstrating process analysis from locating relevant CDM tables to visualizing results using process mining tools. The proposed method can be widely applicable across different institutions. This work can contribute to bringing a process mining perspective to the existing CDM users in the changing Hospital Information Systems (HIS) environment and also to facilitating CDM-based studies in the process mining research community.
Copyright: © 2023 Park et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





References
-
- Dumas M, VanderAalst WM, Hofstede AH. Process-aware information systems: bridging people and software through process technology. John Wiley & Sons.
-
- Rebuge Á, Ferreira DR. Business process analysis in healthcare environments: A methodology based on process mining. Inf Syst. 2012;37(2):99–116.
-
- Kaymak U, Mans R, Van De Steeg T, Dierks M. On process mining in health care. Conf Proc IEEE Int Conf Syst Man Cybern. 2012;1859–64.
-
- Mans RS, van der Aalst WMP, Vanwersch RJB. Process Mining in Healthcare: Evaluating and Exploiting Operational Healthcare Processes. 2015. 79–88 p.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

