Aerobic exercise combined with resistance exercise training improves cardiopulmonary function and blood lipid of patients with breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36595800
- PMCID: PMC9794326
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032391
Aerobic exercise combined with resistance exercise training improves cardiopulmonary function and blood lipid of patients with breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: To compare the therapy effects following the aerobic exercise combined with resistance exercise training (AET + RET) and common care treatment for patients with breast cancer.
Methods: Articles about the effects of AET + RET on the breast cancer patients in 4 online databases were searched. The differences of cardiopulmonary function, blood pressure, blood lipid, and body mass index between the AET + RET treatment and the usual care treatment were compared.
Results: Totally, 8 articles were involved into the meta-analysis. The qualities of the 8 articles were medium. The combination results showed that AET + RET increased the VO2peak (weighted mean difference (WMD) = 2.93 mL/kg/min; 95% CI: 0.38, 5.49; P = .02) and VO2max (WMD = 6.98 mL/kg/min; 95% CI: 2.04, 15.92; P = .01), demonstrating its improving effects in cardiopulmonary function. Moreover, the AET + RET decreased the TG (WMD = -57.95 mg/dL; 95% CI: -112.25, -3.64; P = .04), demonstrating its improving effects in blood lipid. While or the HRpeak, RERpeak, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and body mass index, there are no significant differences between the AET + RET and usual care treatment (P < .05).
Conclusion: Our results demonstrated that AET + RET can significantly improve the cardiopulmonary function and blood lipid for breast cancer patients.
Copyright © 2022 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
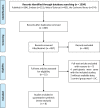
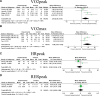


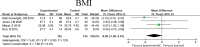
Similar articles
-
Moderators of the effects of exercise training in breast cancer patients receiving chemotherapy: a randomized controlled trial.Cancer. 2008 Apr 15;112(8):1845-53. doi: 10.1002/cncr.23379. Cancer. 2008. PMID: 18306372 Clinical Trial.
-
Feasibility of exercise training for the short-term treatment of generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized controlled trial.Psychother Psychosom. 2012;81(1):21-8. doi: 10.1159/000327898. Epub 2011 Nov 22. Psychother Psychosom. 2012. PMID: 22116310 Clinical Trial.
-
Frequency of combined resistance and aerobic training in older women.J Strength Cond Res. 2013 Jul;27(7):1868-76. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e31827367e0. J Strength Cond Res. 2013. PMID: 22996024 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Exercise Training to Decrease Ectopic Intermuscular Adipose Tissue in Individuals With Chronic Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Phys Ther. 2021 Oct 1;101(10):pzab162. doi: 10.1093/ptj/pzab162. Phys Ther. 2021. PMID: 34174085
-
Estimating the Effect of Aerobic Exercise Training on Novel Lipid Biomarkers: A Systematic Review and Multivariate Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Sports Med. 2023 Apr;53(4):871-886. doi: 10.1007/s40279-023-01817-0. Epub 2023 Mar 2. Sports Med. 2023. PMID: 36862340 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Exercise and cardiovascular health among breast cancer survivors: a scoping review of current observational evidence.Cardiooncology. 2025 Feb 26;11(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s40959-025-00310-z. Cardiooncology. 2025. PMID: 40012001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Physical Activity and Cancer Control (PACC) framework: update on the evidence, guidelines, and future research priorities.Br J Cancer. 2024 Oct;131(6):957-969. doi: 10.1038/s41416-024-02748-x. Epub 2024 Jun 27. Br J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38926526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of lipid metabolism by exercise: exploring its potential as a therapeutic target in cancer endocrinology.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 May 23;16:1580559. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1580559. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40487761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of a Supervised Exercise Program on Pain, Physical Function, and Quality of Life in Patients With Breast Cancer: Protocol for a Randomized Clinical Trial.JMIR Res Protoc. 2025 Mar 12;14:e63891. doi: 10.2196/63891. JMIR Res Protoc. 2025. PMID: 40073395 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of aerobic combined with resistance exercise on cardiorespiratory fitness and cardiometabolic health in breast cancer survivors: A Systematic Review, meta-analysis and meta-regression.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 11;10(4):e26318. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26318. eCollection 2024 Feb 29. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38384575 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rugo HS. Achieving improved survival outcomes in advanced breast cancer. Mass Medical Soc. 2019;381:371–2. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

