Contrast-enhanced ultrasound targeted versus conventional ultrasound guided systematic prostate biopsy for the accurate diagnosis of prostate cancer: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 36595877
- PMCID: PMC9794341
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032404
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound targeted versus conventional ultrasound guided systematic prostate biopsy for the accurate diagnosis of prostate cancer: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Conventional transrectal ultrasonography (TRUS) guided prostate biopsy is the standard method for accurate diagnosis of prostate cancer (PCa). However, the limitations of this technique in terms of missed diagnosis cannot be ignored. Based on previous studies, contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) may be able to more distinctly detect malignant lesions with increased microvessels. Therefore, to evaluate the diagnostic efficiency and clinical application prospects of CEUS-guided prostate biopsy for patients with suspected PCa, we performed a meta-analysis comparing CEUS-targeted with TRUS-guided systematic biopsy.
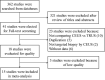
Methods: A systematic search of PubMed, Web of Science, Embase and CNKI was performed up to March, 2022 for the relevant published studies. After data extraction and quality assessment, meta-analysis was performed using the RevMan 5.3 software.
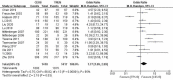
Results: The results showed that the overall sensitivity was higher for CEUS targeted biopsy than systematic biopsy (P = .03), so was the accuracy (P = .03). However, significant heterogeneity and inconsistent results from certain subgroup analyses challenged the validity of the results. Meanwhile, CEUS yielded a much higher sensitivity in patients with prostate specific antigen (PSA) level of 4 to 10 ng/mL (P = .007). On the other hand, the positive rate of each core (P < .001) and the detection rate of clinically significant PCa (P = .006) were significantly improved using CEUS.
Conclusion: CEUS showed the advantage of a higher detection rate of clinically significant PCa, which might provide more specific indications for subsequent treatment. More feasible, real-time data are required to confirm our findings.
Copyright © 2022 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures





References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69:7–34. - PubMed
-
- Holm HH, Gammelgaard J. Ultrasonically guided precise needle placement in the prostate and the seminal vesicles. J Urol. 1981;125:385–7. - PubMed
-
- Giannarini G, Autorino R, di Lorenzo G. Saturation biopsy of the prostate: why saturation does not saturate. Eur Urol. 2009;56:619–21. - PubMed
-
- Goldberg H, Ahmad AE, Chandrasekar T, et al. Comparison of magnetic resonance imaging and transrectal ultrasound informed prostate biopsy for prostate cancer diagnosis in biopsy naive men: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Urol. 2020;203:1085–93. - PubMed
-
- Postema AW, Frinking PJ, Smeenge M, et al. Dynamic contrast-enhanced ultrasound parametric imaging for the detection of prostate cancer. BJU Int. 2016;117:598–603. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

