Protocol to use de-epithelialized porcine urinary bladder as a tissue scaffold for propagation of pancreatic cells
- PMID: 36595896
- PMCID: PMC9692066
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xpro.2022.101869
Protocol to use de-epithelialized porcine urinary bladder as a tissue scaffold for propagation of pancreatic cells
Abstract
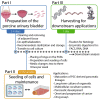
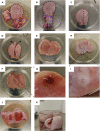
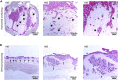
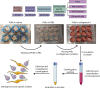
Ex vivo organ culture can be a useful alternative to in vivo models, which can be time-, labor-, and cost-intensive. Here we describe a step-by-step protocol to use de-epithelialized porcine urinary bladders as scaffolds in air-liquid interface in vitro culture systems for a variety of pluripotent stem-cell-derived and patient-derived pancreatic cells and organoids. The scaffold can trigger cell maturation and enable cell-cell interaction and invasion capacity studies. However, this model is limited by the lack of functional vasculature. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Melzer et al. (2022),1 Breunig et al. (2021),2 and Breunig et al. (2021).3.
Keywords: Cell Differentiation; Cell culture; Material sciences; Stem Cells; Tissue Engineering.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Melzer M.K., Breunig M., Arnold F., Wezel F., Azoitei A., Roger E., Krüger J., Merkle J., Schütte L., Resheq Y., et al. Organoids at the PUB: the porcine urinary bladder serves as a pancreatic niche for advanced cancer modeling. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022;11:2102345. doi: 10.1002/ADHM.202102345. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Breunig M., Merkle J., Wagner M., Melzer M.K., Barth T.F.E., Engleitner T., Krumm J., Wiedenmann S., Cohrs C.M., Perkhofer L., et al. Modeling plasticity and dysplasia of pancreatic ductal organoids derived from human pluripotent stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2021;28:1105–1124.e19. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2021.03.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beutel A.K., Schütte L., Scheible J., Roger E., Müller M., Perkhofer L., Kestler A.M.T.U., Kraus J.M., Kestler H.A., Barth T.F.E., et al. A prospective feasibility trial to challenge patient–derived pancreatic cancer organoids in predicting treatment response. Cancers. 2021;13:2539. doi: 10.3390/cancers13112539. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Frappart P.O., Walter K., Gout J., Beutel A.K., Morawe M., Arnold F., Breunig M., Barth T.F., Marienfeld R., Schulte L., et al. Pancreatic cancer-derived organoids – a disease modeling tool to predict drug response. United Euro. Gastroenterol. J. 2020;8:594–606. doi: 10.1177/2050640620905183. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

