Efficacy and safety of endostar combined with cisplatin in treatment of non-small cell lung cancer with malignant pleural effusion: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 36595983
- PMCID: PMC9803422
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032207
Efficacy and safety of endostar combined with cisplatin in treatment of non-small cell lung cancer with malignant pleural effusion: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Although there are new treatments for non-small cell lung cancer with malignant pleural effusion, these therapies are prone to recurrent pleural effusion and poor in efficacy. And recombinant human endostatin is a new type of anti-tumor angiogenesis drug independently developed in my country. It has the effect of inhibiting tumor angiogenesis, inhibiting tumor proliferation and differentiation, and effectively inhibiting the formation and recurrence of malignant pleural effusion. Therefore, this study is aim to systematically review the efficacy and safety of intrapleural injection of endostar combined with cisplatin in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with malignant pleural effusion.
Methods: Databases including Cochrane Library, PubMed, CBM, Embase, CNKI, and WanFang Data were searched to collect randomized controlled trials about endostar combined with cisplatin for NSCLC with malignant pleural effusion from inception to April 2022. Two reviewers independently screened the literature, extracted data, and assessed the risk of bias in included studies. Finally, the meta-analysis was made by using RevMan 5.4.1 software.
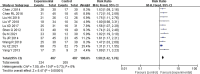
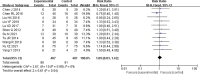
Results: A total of 11 randomized controlled trials involving 814 patients were finally included. The results of the meta-analysis showed that: The overall response rate and the improvement rate of quality of life in the endostar combined with cisplatin group were higher than that of the cisplatin alone group (relative risk = 1.58, 95% confidence interval = 1.42-1.76, P < .00001; relative risk = 1.63, 95% confidence interval = 1.38-1.93, P < .00001, respectively). Meanwhile, there were no significant differences between the 2 groups in the incidence of gastrointestinal reaction, the incidence of leucopenia, the incidence of thrombocytopenia, and the incidence of hypodynamia (all P values > .05).
Conclusion: Compared with cisplatin, intrapleural injection of endostar combined with cisplatin could improve the overall response rate and the quality of life of NSCLC patients with malignant pleural effusion. Due to the limited quality and quantity of included studies, more high-quality studies are needed to verify the above conclusion.
Copyright © 2022 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Effect of thoracic hyperthermic perfusion with recombinant human endostatin plus nedaplatin in treating pleural effusion in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer.J BUON. 2020 Nov-Dec;25(6):2643-2649. J BUON. 2020. PMID: 33455108
-
Thoracic perfusion of lobaplatin combined with endostar for treating malignant pleural effusions: A meta-analysis and systematic review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Oct 7;101(40):e30749. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000030749. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36221355 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of intracavitary administration of Endostar combined with cisplatin in malignant pleural effusion and ascites.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014 Sep;70(1):623-8. doi: 10.1007/s12013-014-9965-9. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014. PMID: 24920191
-
Randomized controlled trial of endostar combined with cisplatin/ pemetrexed chemotherapy for elderly patients with advanced malignant pleural effusion of lung adenocarcinoma.J BUON. 2018 Jan-Feb;23(1):92-97. J BUON. 2018. PMID: 29552766 Clinical Trial.
-
Endostar continuous versus intermittent intravenous infusion combined with chemotherapy for advanced NSCLC: a systematic review and meta-analysis including non-randomized studies.BMC Cancer. 2020 Oct 21;20(1):1021. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07527-4. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33087103 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Thoracic perfusion of antiangiogenic agents combined with chemotherapy for treating malignant pleural effusion in non-small cell lung cancer: a network meta-analysis.BMJ Open. 2024 Dec 20;14(12):e080703. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-080703. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 39806648 Free PMC article.
-
Intrapleural Administration With Rh-Endostatin and Chemical Irritants in the Control of Malignant Pleural Effusion: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2021 Aug 3;11:649999. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.649999. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34414103 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, et al. . Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9–29. - PubMed
-
- Shi SB, Ma TH, Li CH, et al. . Effect of maintenance therapy with dendritic cells: cytokine-induced killer cells in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Tumori. 2012;98:314–9. - PubMed
-
- Duan CX, Liang XG, Zhang ZQ. Efficacy analysis of endorphin combined with cisplatin in the treatment of malignant pleural effusion in non-small cell lung cancer. J Baotou Med College. 2015;31:45–6. (恩度联合顺铂治疗非小细胞肺癌恶性胸腔积液的疗效分析).
-
- Zheng QH, Hu W, Liao XF, et al. . A comparision between intrapleural injection of cisplatin combined with endostar and cisplatin alone in the treatment for malignant pleural effusion. J Chin Oncol. 2013;19:386–9. (顺铂序贯恩度与单纯顺铂胸腔内灌注治疗恶性胸腔积液的临床对照研究).
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S. (eds). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available at: www.cochrane-handbook.org.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

