Efficient generation of lower induced motor neurons by coupling Ngn2 expression with developmental cues
- PMID: 36596304
- PMCID: PMC10117176
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111896
Efficient generation of lower induced motor neurons by coupling Ngn2 expression with developmental cues
Abstract
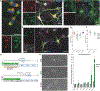
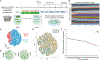
Human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) are a powerful tool for disease modeling of hard-to-access tissues (such as the brain). Current protocols either direct neuronal differentiation with small molecules or use transcription-factor-mediated programming. In this study, we couple overexpression of transcription factor Neurogenin2 (Ngn2) with small molecule patterning to differentiate hPSCs into lower induced motor neurons (liMoNes/liMNs). This approach induces canonical MN markers including MN-specific Hb9/MNX1 in more than 95% of cells. liMNs resemble bona fide hPSC-derived MN, exhibit spontaneous electrical activity, express synaptic markers, and can contact muscle cells in vitro. Pooled, multiplexed single-cell RNA sequencing on 50 hPSC lines reveals reproducible populations of distinct subtypes of cervical and brachial MNs that resemble their in vivo, embryonic counterparts. Combining small molecule patterning with Ngn2 overexpression facilitates high-yield, reproducible production of disease-relevant MN subtypes, which is fundamental in propelling our knowledge of MN biology and its disruption in disease.
Keywords: CP: Neuroscience; CP: Stem cell research; Dropulation; NGN2; differentiation protocol; human stem cells; motor neuron; multiplexed pooled sequencing; neuronal differentiation; patterning molecules; single cell profiling; spinal cord.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests K.E. is cofounder of Q-State Biosciences, Quralis, Enclear Therapies, and is group vice president at BioMarin Pharmaceutical.
Figures





References
-
- Mitchell JM, Nemesh J, Ghosh S, Handsaker RE, Mello CJ, Meyer D, Raghunathan K, de Rivera H, Tegtmeyer M, Hawes D, et al. (2020). Mapping genetic effects on cellular phenotypes with “cell villages”. Preprint at bioRxiv. 10.1101/2020.06.29.174383. - DOI
-
- Wells MF, Nemesh J, Ghosh S, Mitchell JM, Mello CJ, Meyer D, Raghunathan K, Tegtmeyer M, Hawes D, Neumann A, et al. (2021). Natural variation in gene expression and Zika virus susceptibility revealed by villages of neural progenitor cells. Preprint at bioRxiv. 10.1101/2021.11.08.467815. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

