Evaluation of mortality attributable to SARS-CoV-2 vaccine administration using national level data from Qatar
- PMID: 36596793
- PMCID: PMC9808756
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-35653-z
Evaluation of mortality attributable to SARS-CoV-2 vaccine administration using national level data from Qatar
Abstract
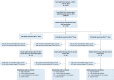
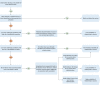
Accurate determination of mortality attributable to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination is critical in allaying concerns about their safety. We reviewed every death in Qatar that occurred within 30 days of any SARS-CoV-2 vaccine administration between January 1, 2021 and June 12, 2022. Probability of association with SARS-CoV-2 vaccination was determined by four independent trained reviewers using a modified WHO algorithm. Among 6,928,359 doses administered, 138 deaths occurred within 30 days of vaccination; eight had a high probability (1.15/1,000,000 doses), 15 had intermediate probability (2.38/1,000,000 doses), and 112 had low probability or no association with vaccination. The death rate among those with high probability of relationship to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination was 0.34/100,000 unique vaccine recipients, while death rate among those with either high or intermediate probability of relationship to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination was 0.98/100,000 unique vaccine recipients. In conclusion, deaths attributable to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination are extremely rare and lower than the overall crude mortality rate in Qatar.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
A.A.B. has received investigator initiated grant funding from Gilead Sciences and Merck and Company (to the institution, Veterans Health Foundation of Pittsburgh) which is unrelated to the work presented here. Other authors declare no conflict of interest regarding the content of this article.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous