Identification of Asymptomatic COVID-19 Patients on Chest CT Images Using Transformer-Based or Convolutional Neural Network-Based Deep Learning Models
- PMID: 36596937
- PMCID: PMC9810383
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-022-00754-0
Identification of Asymptomatic COVID-19 Patients on Chest CT Images Using Transformer-Based or Convolutional Neural Network-Based Deep Learning Models
Abstract
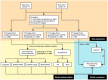
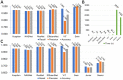
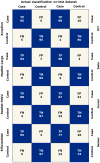
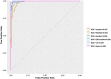
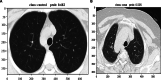
Novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has rapidly spread throughout the world; however, it is difficult for clinicians to make early diagnoses. This study is to evaluate the feasibility of using deep learning (DL) models to identify asymptomatic COVID-19 patients based on chest CT images. In this retrospective study, six DL models (Xception, NASNet, ResNet, EfficientNet, ViT, and Swin), based on convolutional neural networks (CNNs) or transformer architectures, were trained to identify asymptomatic patients with COVID-19 on chest CT images. Data from Yangzhou were randomly split into a training set (n = 2140) and an internal-validation set (n = 360). Data from Suzhou was the external-test set (n = 200). Model performance was assessed by the metrics accuracy, recall, and specificity and was compared with the assessments of two radiologists. A total of 2700 chest CT images were collected in this study. In the validation dataset, the Swin model achieved the highest accuracy of 0.994, followed by the EfficientNet model (0.954). The recall and the precision of the Swin model were 0.989 and 1.000, respectively. In the test dataset, the Swin model was still the best and achieved the highest accuracy (0.980). All the DL models performed remarkably better than the two experts. Last, the time on the test set diagnosis spent by two experts-42 min, 17 s (junior); and 29 min, 43 s (senior)-was significantly higher than those of the DL models (all below 2 min). This study evaluated the feasibility of multiple DL models in distinguishing asymptomatic patients with COVID-19 from healthy subjects on chest CT images. It found that a transformer-based model, the Swin model, performed best.
Keywords: Asymptomatic coronavirus-disease-2019 patients; Chest CT images; Convolutional neural networks; Deep learning; Transfer learning; Transformer.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
COVID-19 Pneumonia Diagnosis Using a Simple 2D Deep Learning Framework With a Single Chest CT Image: Model Development and Validation.J Med Internet Res. 2020 Jun 29;22(6):e19569. doi: 10.2196/19569. J Med Internet Res. 2020. PMID: 32568730 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Learning-Based System Combining Chest X-Ray and Computerized Tomography Images for COVID-19 Diagnosis.Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 2024 Aug 30;85(8):1-15. doi: 10.12968/hmed.2024.0244. Epub 2024 Aug 27. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 2024. PMID: 39212565
-
Enhanced Pneumonia Detection in Chest X-Rays Using Hybrid Convolutional and Vision Transformer Networks.Curr Med Imaging. 2025;21:e15734056326685. doi: 10.2174/0115734056326685250101113959. Curr Med Imaging. 2025. PMID: 39806960
-
Detection of COVID-19 from CT and Chest X-ray Images Using Deep Learning Models.Ann Biomed Eng. 2022 Jul;50(7):825-835. doi: 10.1007/s10439-022-02958-5. Epub 2022 Apr 12. Ann Biomed Eng. 2022. PMID: 35415768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and integration of VGG and dense transfer-learning systems supported with diverse lung images for discovery of the Coronavirus identity.Inform Med Unlocked. 2022;32:101004. doi: 10.1016/j.imu.2022.101004. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Inform Med Unlocked. 2022. PMID: 35822170 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A few-shot learning framework for the diagnosis of osteopenia and osteoporosis using knee X-ray images.J Int Med Res. 2024 Sep;52(9):3000605241274576. doi: 10.1177/03000605241274576. J Int Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39225007 Free PMC article.
-
Dung Beetle Optimization with Deep Feature Fusion Model for Lung Cancer Detection and Classification.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Aug 5;15(15):3982. doi: 10.3390/cancers15153982. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37568800 Free PMC article.
-
Robust Medical Diagnosis: A Novel Two-Phase Deep Learning Framework for Adversarial Proof Disease Detection in Radiology Images.J Imaging Inform Med. 2024 Feb;37(1):308-338. doi: 10.1007/s10278-023-00916-8. Epub 2024 Jan 10. J Imaging Inform Med. 2024. PMID: 38343214 Free PMC article.
-
Automated machine learning for the identification of asymptomatic COVID-19 carriers based on chest CT images.BMC Med Imaging. 2024 Feb 27;24(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s12880-024-01211-w. BMC Med Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38413923 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen G, Lu M, Shi Z, et al. Development and validation of machine learning prediction model based on computed tomography angiography-derived hemodynamics for rupture status of intracranial aneurysms: a Chinese multicenter study. Eur Radiol. 2020;30(9):5170–5182. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-06886-7. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

