Structure and Function of Cationic and Ionizable Lipids for Nucleic Acid Delivery
- PMID: 36600047
- PMCID: PMC9812548
- DOI: 10.1007/s11095-022-03460-2
Structure and Function of Cationic and Ionizable Lipids for Nucleic Acid Delivery
Erratum in
-
Correction: Structure and Function of Cationic and Ionizable Lipids for Nucleic Acid Delivery.Pharm Res. 2024 Jul;41(7):1543-1545. doi: 10.1007/s11095-024-03714-1. Pharm Res. 2024. PMID: 38918310 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
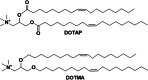
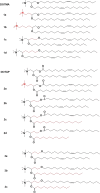
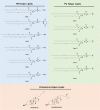
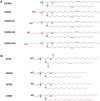
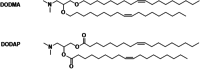
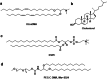
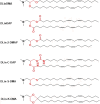
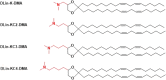
Hereditary genetic diseases, cancer, and infectious diseases are affecting global health and become major health issues, but the treatment development remains challenging. Gene therapies using DNA plasmid, RNAi, miRNA, mRNA, and gene editing hold great promise. Lipid nanoparticle (LNP) delivery technology has been a revolutionary development, which has been granted for clinical applications, including mRNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 infections. Due to the success of LNP systems, understanding the structure, formulation, and function relationship of the lipid components in LNP systems is crucial for design more effective LNP. Here, we highlight the key considerations for developing an LNP system. The evolution of structure and function of lipids as well as their LNP formulation from the early-stage simple formulations to multi-components LNP and multifunctional ionizable lipids have been discussed. The flexibility and platform nature of LNP enable efficient intracellular delivery of a variety of therapeutic nucleic acids and provide many novel treatment options for the diseases that are previously untreatable.
Keywords: cationic lipid; ionizable lipid; lipid nucleic acid nanoparticles; nucleic acid delivery; structural effect.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interests/competing interests for the authors in this work.
Figures



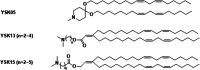


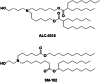
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

