SIGIRR-caspase-8 signaling mediates endothelial apoptosis in Kawasaki disease
- PMID: 36600293
- PMCID: PMC9811794
- DOI: 10.1186/s13052-022-01401-8
SIGIRR-caspase-8 signaling mediates endothelial apoptosis in Kawasaki disease
Abstract
Background: Kawasaki disease (KD) is a kind of vasculitis with unidentified etiology. Given that the current diagnosis and therapeutic strategy of KD are mainly dependent on clinical experiences, further research to explore its pathological mechanisms is warranted.
Methods: Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used to measure the serum levels of SIGIRR, TLR4 and caspase-8. Western blotting was applied to determine protein levels, and flow cytometry was utilized to analyze cell apoptosis. Hematoxylin eosin (HE) staining and TUNEL staining were respectively used to observe coronary artery inflammation and DNA fragmentation.
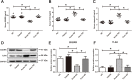
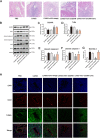
Results: In this study, we found the level of SIGIRR was downregulated in KD serum and KD serum-treated endothelial cells. However, the level of caspase-8 was increased in serum from KD patients compared with healthy control (HC). Therefore, we hypothesized that SIGIRR-caspase-8 signaling may play an essential role in KD pathophysiology. In vitro experiments demonstrated that endothelial cell apoptosis in the setting of KD was associated with caspase-8 activation, and SIGIRR overexpression alleviated endothelial cell apoptosis via inhibiting caspase-8 activation. These findings were also recapitulated in the Candida albicans cell wall extracts (CAWS)-induced KD mouse model.
Conclusion: Our data suggest that endothelial cell apoptosis mediated by SIGIRR-caspase-8 signaling plays a crucial role in coronary endothelial damage, providing potential targets to treat KD.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Caspase-8; Endothelial cell; Kawasaki disease; SIGIRR.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures




References
-
- He M, Chen Z, Martin M, Zhang J, Sangwung P, Woo B, Tremoulet AH, Shimizu C, Jain MK, Burns JC, Shyy JY. MiR-483 Targeting of CTGF Suppresses Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition: Therapeutic Implications in Kawasaki Disease. Circ Res. 2017;120:354–365. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.310233. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chu M, Wu R, Qin S, Hua W, Shan Z, Rong X, Zeng J, Hong L, Sun Y, Liu Y, Li W, Wang S, Zhang C. Bone Marrow-Derived MicroRNA-223 Works as an Endocrine Genetic Signal in Vascular Endothelial Cells and Participates in Vascular Injury From Kawasaki Disease. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017;6:1–14. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.116.004878. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

