Prognostic value of tumor-associated N1/N2 neutrophil plasticity in patients following radical resection of pancreas ductal adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 36600557
- PMCID: PMC9730407
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2022-005798
Prognostic value of tumor-associated N1/N2 neutrophil plasticity in patients following radical resection of pancreas ductal adenocarcinoma
Abstract
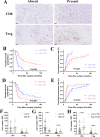
Background: As an integral part of the tumor microenvironment (TME), tumor-associated neutrophils play a crucial role in tumor development. The objective of this study was to investigate the plasticity of tumor-associated N1 and N2 neutrophils in the TME of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), along with its impact on survival and association with immune infiltrations.
Methods: The primary and validation cohorts including 90 radical resection patients from September 2012 to May 2016 and 29 radical resection patients from September 2018 to October 2019, respectively, with complete survival data, were enrolled. Immunofluorescence staining was used to identify tumor-associated N1 and N2 neutrophils, and the N1/N2 ratio was used to evaluate N1 and N2 plasticity. Thereafter, the association between tumor-associated N1/N2 neutrophil plasticity, clinical features, and immune infiltrations was investigated.
Results: There was a significant increase in tumor-associated N2 neutrophils compared with tumor-associated N1 neutrophils. Low N1/N2 ratios were associated with the poorer differentiation of tumors, easier lymph node metastases, and a higher TNM stage. The median overall survival (OS) and recurrence-free survival (RFS) of the high tumor-associated N1 neutrophil group were significantly longer than those of the low group, while the tumor-associated N2 neutrophils played an opposite role. The multivariable analysis revealed that a high N1/N2 ratio was a significant prognostic indicator for OS and RFS. In addition, tumor-associated N1/N2 neutrophils showed an opposite correlation with tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells and Tregs.
Conclusion: The plasticity of tumor-associated N1/N2 neutrophils was identified as a crucial prognostic indicator that might reflect the TME and immune escape in patients with PDAC. On further investigation and validation, our findings may be used to further stratify patients with varying prognoses to optimize treatment.
Keywords: Tumor Biomarkers; Tumor Microenvironment.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prognostic significance and immune escape implication of tumor-infiltrating neutrophil plasticity in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Hum Cell. 2024 May;37(3):714-728. doi: 10.1007/s13577-024-01024-7. Epub 2024 Feb 15. Hum Cell. 2024. PMID: 38358636
-
Prognostic Value of N1/N2 Neutrophils Heterogeneity and Tertiary Lymphoid Structure in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients.Cancer Med. 2024 Dec;13(24):e70551. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70551. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 39718130 Free PMC article.
-
Lymph Node Metastatic Patterns and Survival Predictors Based on Tumor Size in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Adv Ther. 2021 Aug;38(8):4258-4270. doi: 10.1007/s12325-021-01819-2. Epub 2021 Jun 26. Adv Ther. 2021. PMID: 34176089
-
Neutrophil in the Pancreatic Tumor Microenvironment.Biomolecules. 2021 Aug 7;11(8):1170. doi: 10.3390/biom11081170. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34439836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutrophils as key regulators of tumor microenvironment in breast cancer: a focus on N1 and N2 polarization.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2025 Apr 10;87(6):3509-3522. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000003269. eCollection 2025 Jun. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40486595 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The predictive value of prognosis and therapeutic response for STAT family in pancreatic cancer.Heliyon. 2023 May 12;9(5):e16150. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16150. eCollection 2023 May. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37215832 Free PMC article.
-
Yiqi Huayu Jiedu Decoction reduces colorectal cancer liver metastasis by promoting N1 neutrophil chemotaxis.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 27;16:1530053. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1530053. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40083557 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Microfluidic Chip for Neutrophil Extracellular Vesicle Analysis and Gastric Cancer Diagnosis.ACS Nano. 2025 Mar 18;19(10):10078-10092. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.4c16894. Epub 2025 Mar 9. ACS Nano. 2025. PMID: 40059332 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of silencing eEF2K expression on the malignant properties of chordoma.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Apr;50(4):3011-3022. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08257-z. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36652154
-
Immunocytes in the tumor microenvironment: recent updates and interconnections.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 14;16:1517959. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1517959. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40297580 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
