Development and Validation of Prognostic Nomograms for Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Hepatectomy Based on Inflammatory Markers
- PMID: 36600988
- PMCID: PMC9807130
- DOI: 10.2147/JHC.S390858
Development and Validation of Prognostic Nomograms for Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Hepatectomy Based on Inflammatory Markers
Abstract
Background: The value of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) compared with other inflammation-based scores in predicting the outcomes of hepatitis B virus (HBV)-related hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients after curative resection remains unknown. This study aims to evaluate the predictive value of LDH and develop novel nomograms to predict postoperative recurrence and survival in these patients.
Methods: This study retrospectively collected 1560 patients with HBV-related HCC who underwent curative resection from four institutions in China. In total, 924 patients were recruited from our center and randomly divided into the training cohort (n = 616) and internal validation (n = 308) cohorts. Additionally, 636 patients were selected from three other centers as the external validation cohort. The C index of inflammation-based scores was calculated and compared in the training cohort. Novel models were developed according to multivariable Cox regression analysis in the training cohort and validated in the internal and external validation cohorts.
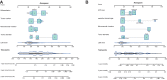
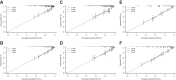
Results: LDH showed a higher C-index than other inflammation-based scores for recurrence survival (RFS, 0.60, 95% CI, 0.58-0.61) and overall survival (OS, 0.65, 95% CI, 0.63-0.68). The nomograms of RFS and OS were developed based on tumor diameter, macrovascular invasion, AFP, operative hemorrhage, tumor differentiation, tumor number and LDH and achieved a high C-index (0.78, 95% CI, 0.76-0.79 and 0.81, 95% CI, 0.79-0.83), which were remarkably higher than the C-indexes of the five conventional HCC staging systems (0.52-0.62 for RFS and 0.53-0.67 for OS). The nomograms were validated in the internal validation cohort (0.77 for RFS, 0.78 for OS) and external validation cohort (0.80 for RFS, 0.81 for OS) and performed well-fitted calibration curves.
Conclusion: The two nomograms based on inflammatory markers achieved optimal prediction for RFS and OS of patients with HBV-related HCC after hepatectomy.
Keywords: hepatectomy; hepatocellular carcinoma; inflammation-based scores; lactate dehydrogenase; nomogram.
© 2022 Hu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare in this work.
Figures


References
-
- Akinyemiju T, Abera S, Ahmed M., et al. The burden of primary liver cancer and underlying etiologies from 1990 to 2015 at the global, regional, and national level results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. JAMA Oncology. 2017;3(12):1683–1691. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.3055 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fitzmaurice C, Abate D, Abbasi N, et al. Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 29 cancer groups, 1990 to 2017 a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA Oncology. 2019;5(12):1749–1768. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.2996 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vos T, Abajobir AA, Abate KH. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. 2017;390(10100):1211–1259. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32154-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

