Glutamine mitigates murine burn sepsis by supporting macrophage M2 polarization through repressing the SIRT5-mediated desuccinylation of pyruvate dehydrogenase
- PMID: 36601059
- PMCID: PMC9801296
- DOI: 10.1093/burnst/tkac041
Glutamine mitigates murine burn sepsis by supporting macrophage M2 polarization through repressing the SIRT5-mediated desuccinylation of pyruvate dehydrogenase
Abstract
Background: Alternative (M2)-activated macrophages drive the anti-inflammatory response against sepsis, a leading cause of death in patients suffering from burn injury. Macrophage M2 polarization is intrinsically linked with dominant oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). Glutamine serves as a major anaplerotic source to fuel OXPHOS, but it remains unknown whether glutamine can modulate metabolic checkpoints in OXPHOS that favour M2 polarization. The study aims to explore whether glutamine essentially supports M2 polarization in IL-4-stimulated murine macrophages by sustaining the activity of PDH and whether glutamine augments macrophage M2 polarization and thus alleviates inflammation and organ injury in a murine burn sepsis model.
Methods: To understand how glutamine promotes M2 activation in interleukin (IL-4)-treated murine macrophages, we detected glutamine-dependent M2 polarization and its relationship with the pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) complex by RT-PCR, flow cytometry and western blot. To explore how glutamine modulates PDH activity and thus supports M2 polarization, we compared the expression, phosphorylation and succinylation status of PDHA1 and then examined sirtuin SIRT5-dependent desuccinylation of PDHA1 and the effects of SIRT5 overexpression on M2 polarization by RT-PCR, flow cytometry and western blot. To determine whether glutamine or its metabolites affect M2 polarization, macrophages were cocultured with metabolic inhibitors, and then SIRT5 expression and M2 phenotype markers were examined by RT-PCR, flow cytometry and western blot. Finally, to confirm the in vivo effect of glutamine, we established a burn sepsis model by injecting Pseudomonas aeruginosa into burn wounds and observing whether glutamine alleviated proinflammatory injuries by RT-PCR, flow cytometry, western blot, immunofluorescent staining, hematoxylin-eosin staining and enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay.
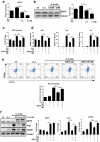
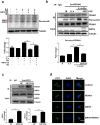
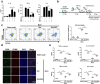
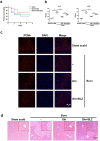
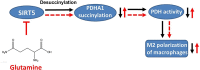
Results: We showed that consumption of glutamine supported M2 activation in IL-4-treated murine macrophages by upregulating the activity of PDH. Mechanistically, glutamine did not affect the expression or alter the phosphorylation status of PDHA1 but instead downregulated the expression of SIRT5 and repressed SIRT5-dependent desuccinylation on PDHA1, which in turn recovered PDH activity and supported M2 polarization. This effect was implemented by its secondary metabolite α-ketoglutarate (αKG) rather than glutamine itself. Finally, we demonstrated that glutamine promoted macrophage M2 polarization in a murine burn sepsis model, thereby repressing excessive inflammation and alleviating organ injury in model mice.
Conclusions: Glutamine mitigates murine burn sepsis by essentially supporting macrophage M2 polarization, with a mechanism involving the repression of the SIRT5-mediated desuccinylation of pyruvate dehydrogenase that replenishes OXPHOS and sustains M2 macrophages.
Keywords: Burn, Sepsis; Desuccinylation; Glutamine; Macrophages polarization; PDH; SIRT5.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Moxibustion Alleviates Inflammation via SIRT5-mediated Post-translational Modification and Macrophage Polarization.Inflammation. 2025 Feb 3. doi: 10.1007/s10753-025-02239-y. Online ahead of print. Inflammation. 2025. PMID: 39899130
-
SIRT5 exacerbates eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis by promoting polarization of M2 macrophage.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2024 Sep;154(3):644-656. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2024.04.028. Epub 2024 May 16. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38761998
-
Norisoboldine Attenuates Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Modulating Macrophage Polarization via PKM2/HIF-1α/PGC-1α Pathway.Biol Pharm Bull. 2021;44(10):1536-1547. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b21-00457. Biol Pharm Bull. 2021. PMID: 34602563
-
SIRT5 -mediated desuccinylation of UQCRC2 attenuates osteogenic differentiation of aged BM-MSCs through impairing mitochondrial homeostasis.Cell Signal. 2025 Apr;128:111636. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2025.111636. Epub 2025 Jan 30. Cell Signal. 2025. PMID: 39892725
-
SIRT5-mediated ME2 desuccinylation promotes cancer growth by enhancing mitochondrial respiration.Cell Death Differ. 2024 Jan;31(1):65-77. doi: 10.1038/s41418-023-01240-y. Epub 2023 Nov 25. Cell Death Differ. 2024. PMID: 38007551 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial metabolic regulation of macrophage polarization in osteomyelitis and other orthopedic disorders: mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Jun 13;13:1604320. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1604320. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40584964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-translational modifications in sepsis-induced organ dysfunction: mechanisms and implications.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 21;15:1461051. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1461051. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39234245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic mechanisms orchestrated by Sirtuin family to modulate inflammatory responses.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 20;15:1448535. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1448535. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39372420 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lactate metabolic reprogramming and histone lactylation modification in sepsis.Int J Biol Sci. 2025 Jul 28;21(11):5034-5055. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.116088. eCollection 2025. Int J Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40860191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial dynamics at the intersection of macrophage polarization and metabolism.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 24;16:1520814. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1520814. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40196123 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

