Construction of prediction model of inflammation related genes in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and its correlation with immune microenvironment
- PMID: 36601116
- PMCID: PMC9806212
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1010345
Construction of prediction model of inflammation related genes in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and its correlation with immune microenvironment
Abstract
Background: The role of inflammation in the formation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) has gained a lot of attention recently. However, the involvement of genes related to inflammation and immune exchange environment status in the prognosis of IPF remains to be further clarified. The objective of this research is to establish a new model for the prediction of the overall survival (OS) rate of inflammation-related IPF.
Methods: Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) was employed to obtain the three expression microarrays of IPF, including two from alveolar lavage fluid cells and one from peripheral blood mononuclear cells. To construct the risk assessment model of inflammation-linked genes, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (lasso), univariate cox and multivariate stepwise regression, and random forest method were used. The proportion of immune cell infiltration was evaluated by single sample Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (ssGSEA) algorithm.
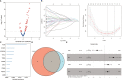
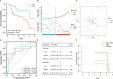
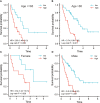
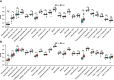
Results: The value of genes linked with inflammation in the prognosis of IPF was analyzed, and a four-genes risk model was constructed, including tpbg, Myc, ffar2, and CCL2. It was highlighted by Kaplan Meier (K-M) survival analysis that patients with high-risk scores had worse overall survival time in all training and validation sets, and univariate and multivariate analysis highlighted that it has the potential to act as an independent risk indicator for poor prognosis. ROC analysis showed that the prediction efficiency of 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS time in the training set reached 0.784, 0.835, and 0.921, respectively. Immune infiltration analysis showed that Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells (MDSC), macrophages, regulatory T cells, cd4+ t cells, neutrophils, and dendritic cells were more infiltrated in the high-risk group than in the low-risk group.
Conclusion: Inflammation-related genes can be well used to evaluate the IPF prognosis and impart a new idea for the treatment and follow-up management of IPF patients.
Keywords: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; immune microenvironment; inflammation; prognosis; ssGSEA.
Copyright © 2022 Yin, Peng, Situ, Xie, Tan, Wei, Jiang, Zhang and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Investigation of a Hypoxia-Immune-Related Microenvironment Gene Signature and Prediction Model for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 14;12:629854. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.629854. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34194423 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and validation of autophagy-related gene expression for predicting prognosis in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 20;13:997138. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.997138. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36211385 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of tripartite motif (TRIM) family gene signature from bronchoalveolar lavage cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.BMC Pulm Med. 2022 Dec 6;22(1):467. doi: 10.1186/s12890-022-02269-4. BMC Pulm Med. 2022. PMID: 36474231 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Immune Cells in the Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Nov 10;59(11):1984. doi: 10.3390/medicina59111984. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 38004032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolving Perspectives on Innate Immune Mechanisms of IPF.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Aug 9;8:676569. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.676569. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34434962 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of oxidative stress-related genes in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 18;15(1):5954. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-89770-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39966531 Free PMC article.
-
Role of inflammation-related genes as prognostic biomarkers and mechanistic implications in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Front Genet. 2025 Jun 18;16:1602588. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1602588. eCollection 2025. Front Genet. 2025. PMID: 40606673 Free PMC article.
-
Updates on the controversial roles of regulatory lymphoid cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 25;15:1466901. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1466901. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39386201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of PANoptosis-related genes for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis by machine learning and molecular subtype analysis.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 14;14(1):24068. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76263-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39402203 Free PMC article.
-
The role and therapeutic targeting of the CCL2/CCR2 signaling axis in inflammatory and fibrotic diseases.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 9;15:1497026. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1497026. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39850880 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

