Simultaneous Use of Endobronchial and Endoscopic Ultrasound Guidance as Primary Tools in the Diagnosis of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma
- PMID: 36601180
- PMCID: PMC9805368
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.32110
Simultaneous Use of Endobronchial and Endoscopic Ultrasound Guidance as Primary Tools in the Diagnosis of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma
Abstract
Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) is related to exposure to asbestos. It is insidious in nature and is generally diagnosed at an advanced stage. MPM is aggressive and portends a poor prognosis. Definitive diagnosis is usually established by obtaining pathological samples of the pleura by medical or surgical thoracoscopy. However, these procedures are invasive and carry a risk of seeding of biopsy sites with tumors. We herein report an infrequently encountered case of simultaneous use of endobronchial ultrasound and endoscopic ultrasound-guided biopsy of malignant pleural mesothelioma in a 48-year-old female patient.
Keywords: endobronchial ultrasound; endoscopic ultrasound; malignant pleural mesothelioma; pleural biopsy; pleural effusion.
Copyright © 2022, Mankidy et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

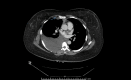
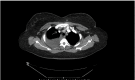
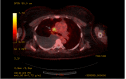
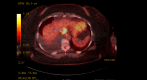
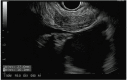

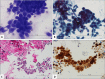
Similar articles
-
[Endobronchial ultrasound in the diagnosis of malignant pleural mesothelioma].Rev Mal Respir. 2015 Sep;32(7):750-4. doi: 10.1016/j.rmr.2014.12.009. Epub 2015 Jun 9. Rev Mal Respir. 2015. PMID: 26071130 French.
-
Pleural mesothelioma: When echo-endoscopy (EUS-B-FNA) leads to diagnosis in a minimally invasive way.Thorac Cancer. 2021 Mar;12(6):981-984. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13868. Epub 2021 Feb 3. Thorac Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33533181 Free PMC article.
-
"Dry" pleural mesothelioma successfully diagnosed on endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS)-guided transbronchial needle aspiration (TBNA).Intern Med. 2014;53(5):467-9. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.53.1563. Intern Med. 2014. PMID: 24583437
-
Endoscopic diagnosis and management of pleural effusion in malignant pleural mesothelioma.J Thorac Dis. 2018 Jan;10(Suppl 2):S269-S275. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2017.09.142. J Thorac Dis. 2018. PMID: 29507795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Medical Thoracoscopy, Computed Tomography-guided Biopsy, and Ultrasound-guided Biopsy for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: A Systematic Review.Anticancer Res. 2021 May;41(5):2217-2225. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.14998. Anticancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33952448
References
-
- US mesothelioma patterns 1973-2002: indicators of change and insights into background rates. Teta MJ, Mink PJ, Lau E, Sceurman BK, Foster ED. Eur J Cancer Prev. 2008;17:525–534. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Incidence of Malignant Mesothelioma, 1999-2018. USCS Data Brief, no. 27. Atlanta, GA: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US Department of Health and Human Services. [ Nov; 2022 ]. 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/uscs/about/data-briefs/no27-incidence-maligna... https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/uscs/about/data-briefs/no27-incidence-maligna...
-
- Thoracoscopy in pleural malignant mesothelioma: a prospective study of 188 consecutive patients. Part 1: Diagnosis. Boutin C, Rey F. https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/uscs/about/data-briefs/no27-incidence-maligna... Cancer. 1993;72:389–393. - PubMed
-
- Update on malignant pleural mesothelioma. Campbell NP, Kindler HL. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;32:102–110. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
