Are Accuracy Studies for Periprosthetic Joint Infection Diagnosis Inherently Flawed? And What to Do with Schrödinger's Hips? A Prospective Analysis of the Alpha Defensin Lateral-Flow Test in Chronic Painful Hip Arthroplasties
- PMID: 36601610
- PMCID: PMC9763830
- DOI: 10.5371/hp.2022.34.4.236
Are Accuracy Studies for Periprosthetic Joint Infection Diagnosis Inherently Flawed? And What to Do with Schrödinger's Hips? A Prospective Analysis of the Alpha Defensin Lateral-Flow Test in Chronic Painful Hip Arthroplasties
Abstract
Purpose: The most recent diagnostic criteria for periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) include the use of the alpha-defensin (AD) lateral-flow (LF) test, but hip and knee arthroplasties were usually combined in previous studies. This prospective study was designed to examine the accuracy of the AD-LF test for diagnosis of PJI in chronic painful total hip arthroplasties (THA).
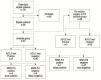
Materials and methods: Patients with chronic painful hip arthroplasties were prospectively enrolled between March 2018 and May 2020. Exclusion criteria included acute PJI or an insufficient amount of synovial fluid. The modified Musculoskeletal Infection Society (MSIS) criteria were primarily used for PJI diagnosis. Fifty-seven patients were included in the analysis group. Revision surgery was not performed in 38 patients, for different reasons (clinical group); these patients remain "Schrödinger's hips": in such cases PJI cannot be excluded nor confirmed until you "open the box".
Results: The result of the AD-LF test was positive in nine patients and negative in 48 patients. Six patients were diagnosed with PJI. AD-LF sensitivity (MSIS criteria) was 83% (95% confidence interval [CI] 36-100%) and specificity was 92% (95% CI 81-98%). The positive and negative predictive value were 56% and 98%, respectively.
Conclusion: The AD test is useful in addition to the existing arsenal of diagnostic tools, and can be helpful in the decision-making process. Not all patients with chronical painful THA will undergo revision surgery. Consequently, in order to determine the reliable diagnostic accuracy of this test, future PJI diagnostic studies should include a second arm of "Schrödinger's hips".
Keywords: Alpha-defensin; Arthroplasty; Diagnosis; Hip; Prosthesis-related infections.
Copyright © 2022 by Korean Hip Society.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: The authors declare that there is no potential conflict of interest relevant to this article.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

