Hybrid height and slope figuring method for grazing-incidence reflective optics
- PMID: 36601927
- PMCID: PMC9814051
- DOI: 10.1107/S160057752201058X
Hybrid height and slope figuring method for grazing-incidence reflective optics
Abstract
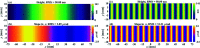
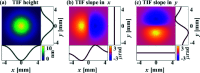
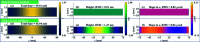
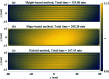
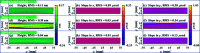
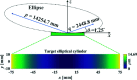
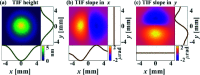
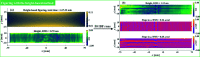
Grazing-incidence reflective optics are commonly used in synchrotron radiation and free-electron laser facilities to transport and focus the emitted X-ray beams. To preserve the imaging capability at the diffraction limit, the fabrication of these optics requires precise control of both the residual height and slope errors. However, all the surface figuring methods are height based, lacking the explicit control of surface slopes. Although our preliminary work demonstrated a one-dimensional (1D) slope-based figuring model, its 2D extension is not straightforward. In this study, a novel 2D slope-based figuring method is proposed, which employs an alternating objective optimization on the slopes in the x- and y-directions directly. An analytical simulation revealed that the slope-based method achieved smaller residual slope errors than the height-based method, while the height-based method achieved smaller residual height errors than the slope-based method. Therefore, a hybrid height and slope figuring method was proposed to further enable explicit control of both the height and slopes according to the final mirror specifications. An experiment to finish an elliptical-cylindrical mirror using the hybrid method with ion beam figuring was then performed. Both the residual height and slope errors converged below the specified threshold values, which verified the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed ideas.
Keywords: ion beam figuring; surface slopes; synchrotron optics; two-dimensional.
open access.
Figures






References
-
- Adapa, B. R., Dovillaire, G., Vivo, A., Perrin, F., Mayer, R. & Barrett, R. (2021). Rev. Sci. Instrum. 92, 113103. - PubMed
-
- Alcock, S., Sawhney, K., Scott, S., Pedersen, U., Walton, R., Siewert, F., Zeschke, T., Senf, F., Noll, T. & Lammert, H. (2010). Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A, 616, 224–228.
-
- Ali, Z. & Yashchuk, V. V. (2011). Report LBNL-5587E. Lawrence Berkeley National Lab.oratory, Berkeley, CA, USA.
-
- Huang, L., Idir, M., Zuo, C., Kaznatcheev, K., Zhou, L. & Asundi, A. (2015). Opt. Lasers Eng. 64, 1–11.
-
- Huang, L., Wang, T., Nicolas, J., Polack, F., Zuo, C., Nakhoda, K. & Idir, M. (2020). Opt. Express, 28, 23060–23074. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

