Cyclic AMP-Mediated Inhibition of Cholesterol Catabolism in Mycobacterium tuberculosis by the Novel Drug Candidate GSK2556286
- PMID: 36602336
- PMCID: PMC9872607
- DOI: 10.1128/aac.01294-22
Cyclic AMP-Mediated Inhibition of Cholesterol Catabolism in Mycobacterium tuberculosis by the Novel Drug Candidate GSK2556286
Abstract
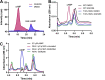
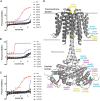
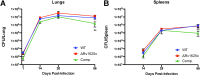
Despite the deployment of combination tuberculosis (TB) chemotherapy, efforts to identify shorter, nonrelapsing treatments have resulted in limited success. Recent evidence indicates that GSK2556286 (GSK286), which acts via Rv1625c, a membrane-bound adenylyl cyclase in Mycobacterium tuberculosis, shortens treatment in rodents relative to standard of care drugs. Moreover, GSK286 can replace linezolid in the three-drug, Nix-TB regimen. Given its therapeutic potential, we sought to better understand the mechanism of action of GSK286. The compound blocked growth of M. tuberculosis in cholesterol media and increased intracellular cAMP levels ~50-fold. GSK286 did not inhibit growth of an rv1625c transposon mutant in cholesterol media and did not induce cyclic AMP (cAMP) production in this mutant, suggesting that the compound acts on this adenylyl cyclase. GSK286 also induced cAMP production in Rhodococcus jostii RHA1, a cholesterol-catabolizing actinobacterium, when Rv1625c was heterologously expressed. However, these elevated levels of cAMP did not inhibit growth of R. jostii RHA1 in cholesterol medium. Mutations in rv1625c conferred cross-resistance to GSK286 and the known Rv1625c agonist, mCLB073. Metabolic profiling of M. tuberculosis cells revealed that elevated cAMP levels, induced using either an agonist or a genetic tool, did not significantly affect pools of steroid metabolites in cholesterol-incubated cells. Finally, the inhibitory effect of agonists was not dependent on the N-acetyltransferase MtPat. Together, these data establish that GSK286 is an Rv1625c agonist and sheds light on how cAMP signaling can be manipulated as a novel antibiotic strategy to shorten TB treatments. Nevertheless, the detailed mechanism of action of these compounds remains to be elucidated.
Keywords: TB; adenylyl cyclase; antibiotic; antitubercular.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare a conflict of interest. Olalla Sanz, Esther Pérez-Herrán, David Barros and Lluís Ballell are employees of GlaxoSmithKline.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization. 2022. Global tuberculosis report, 2022. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland.
-
- Conradie F, Diacon AH, Ngubane N, Howell P, Everitt D, Crook AM, Mendel CM, Egizi E, Moreira J, Timm J, McHugh TD, Wills GH, Bateson A, Hunt R, Van Niekerk C, Li M, Olugbosi M, Spigelman M, Nix TBTT, Nix-TB Trial Team . 2020. Treatment of highly drug-resistant pulmonary tuberculosis. N Engl J Med 382:893–902. 10.1056/NEJMoa1901814. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nuermberger EL, Martinez-Martinez MS, Sanz O, Urones B, Esquivias J, Soni H, Tasneen R, Tyagi S, Li SY, Converse PJ, Boshoff HI, Robertson GT, Besra GS, Abrahams KA, Upton AM, Mdluli K, Boyle GW, Turner S, Fotouhi N, Cammack NC, Siles JM, Alonso M, Escribano J, Lelievre J, Rullas-Trincado J, Perez-Herran E, Bates RH, Maher-Edwards G, Barros D, Ballell L, Jimenez E. 2022. GSK2556286 is a novel antitubercular drug candidate effective in vivo with the potential to shorten tuberculosis treatment. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 66:e00132-22. 10.1128/aac.00132-22. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pethe K, Sequeira PC, Agarwalla S, Rhee K, Kuhen K, Phong WY, Patel V, Beer D, Walker JR, Duraiswamy J, Jiricek J, Keller TH, Chatterjee A, Tan MP, Ujjini M, Rao SPS, Camacho L, Bifani P, Mak PA, Ma I, Barnes SW, Chen Z, Plouffe D, Thayalan P, Ng SH, Au M, Lee BH, Tan BH, Ravindran S, Nanjundappa M, Lin X, Goh A, Lakshminarayana SB, Shoen C, Cynamon M, Kreiswirth B, Dartois V, Peters EC, Glynne R, Brenner S, Dick T. 2010. A chemical genetic screen in Mycobacterium tuberculosis identifies carbon-source-dependent growth inhibitors devoid of in vivo efficacy. Nat Commun 1:57. 10.1038/ncomms1060. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- VanderVen BC, Fahey RJ, Lee W, Liu Y, Abramovitch RB, Memmott C, Crowe AM, Eltis LD, Perola E, Deininger DD, Wang T, Locher CP, Russell DG. 2015. Novel inhibitors of cholesterol degradation in Mycobacterium tuberculosis reveal how the bacterium’s metabolism is constrained by the intracellular environment. PLoS Pathog 11:e1004679. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004679. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

