Vascular mechanotransduction
- PMID: 36603156
- PMCID: PMC9942936
- DOI: 10.1152/physrev.00053.2021
Vascular mechanotransduction
Abstract
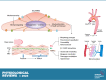
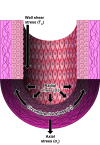
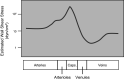
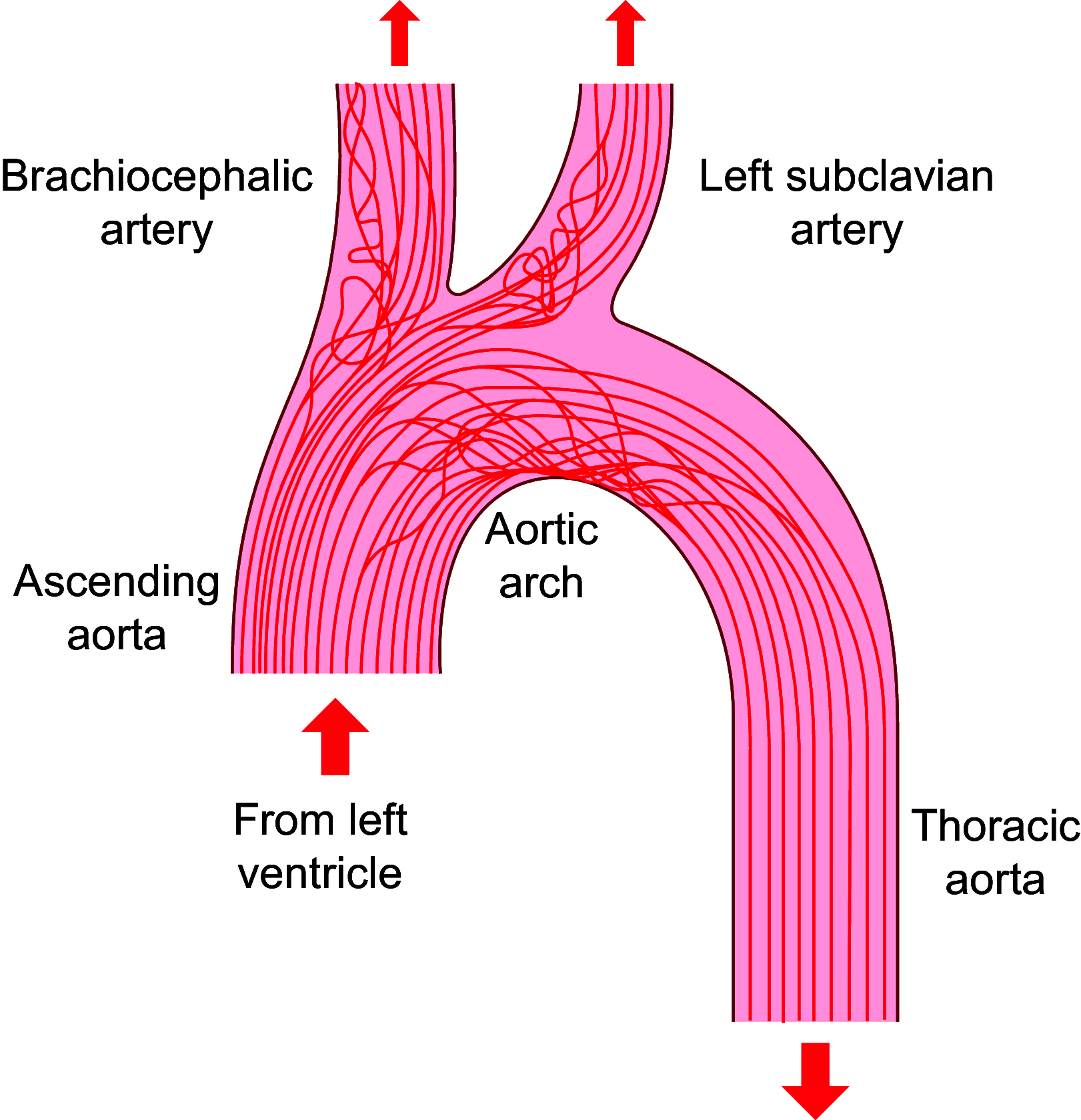
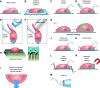
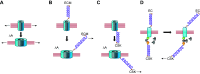
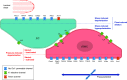
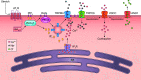
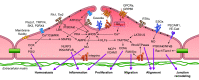
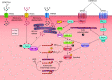
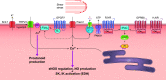
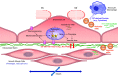
This review aims to survey the current state of mechanotransduction in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) and endothelial cells (ECs), including their sensing of mechanical stimuli and transduction of mechanical signals that result in the acute functional modulation and longer-term transcriptomic and epigenetic regulation of blood vessels. The mechanosensors discussed include ion channels, plasma membrane-associated structures and receptors, and junction proteins. The mechanosignaling pathways presented include the cytoskeleton, integrins, extracellular matrix, and intracellular signaling molecules. These are followed by discussions on mechanical regulation of transcriptome and epigenetics, relevance of mechanotransduction to health and disease, and interactions between VSMCs and ECs. Throughout this review, we offer suggestions for specific topics that require further understanding. In the closing section on conclusions and perspectives, we summarize what is known and point out the need to treat the vasculature as a system, including not only VSMCs and ECs but also the extracellular matrix and other types of cells such as resident macrophages and pericytes, so that we can fully understand the physiology and pathophysiology of the blood vessel as a whole, thus enhancing the comprehension, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of vascular diseases.
Keywords: endothelial cells; flow-induced vasodilation; shear stress; vascular myogenic response; vascular smooth muscle cells.
Conflict of interest statement
S. Earley is an editor of
Figures
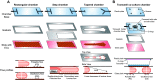
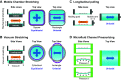
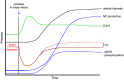
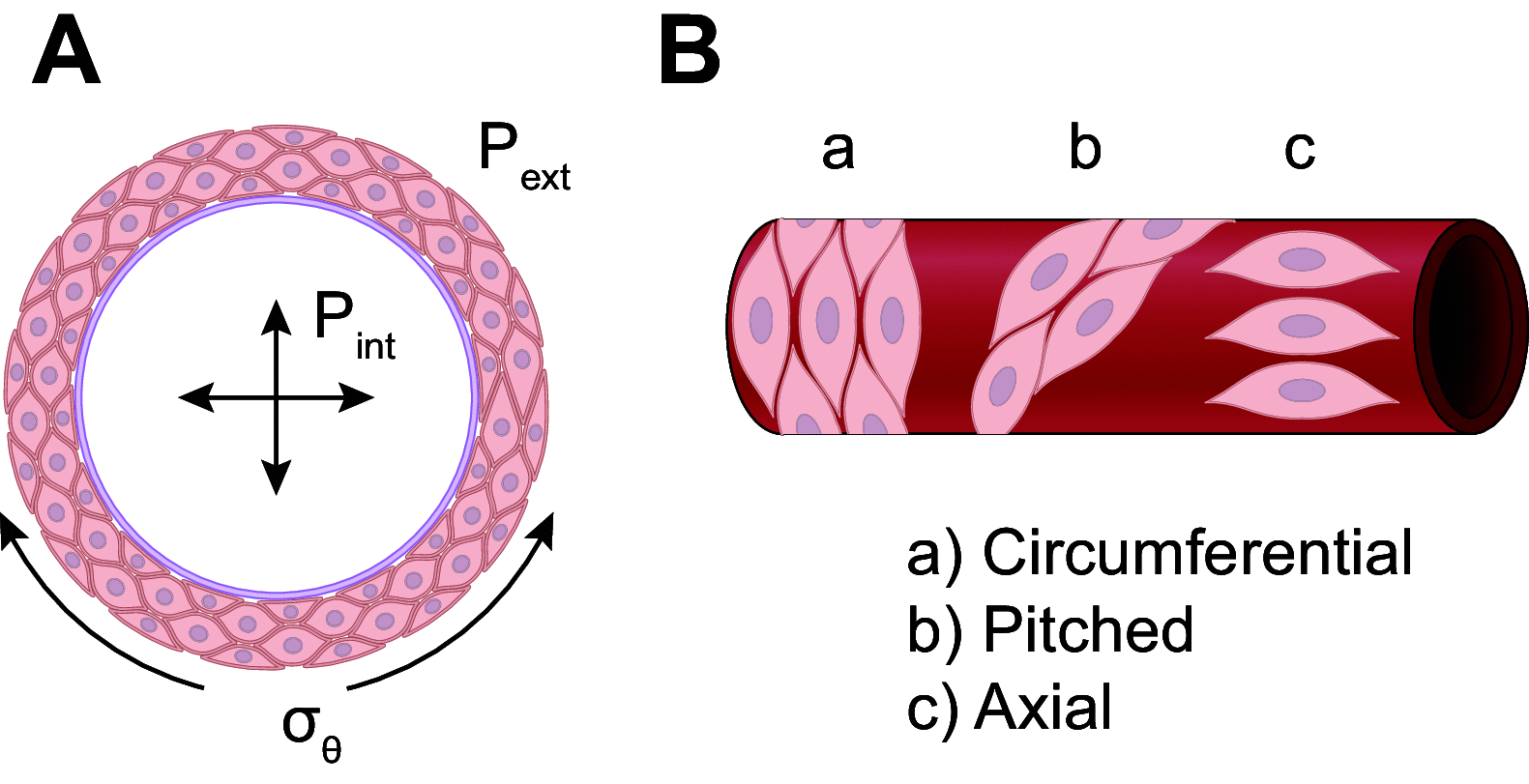

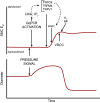
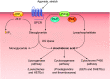
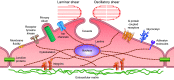
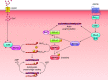


Comment in
-
Is Notch1 a neglected vascular mechanosensor?Physiol Rev. 2024 Apr 1;104(2):655-658. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00033.2023. Epub 2023 Nov 9. Physiol Rev. 2024. PMID: 37943247 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

