A cognitive process modeling framework for the ABCD study stop-signal task
- PMID: 36603413
- PMCID: PMC9826813
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dcn.2022.101191
A cognitive process modeling framework for the ABCD study stop-signal task
Abstract
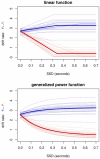
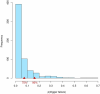
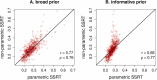
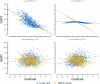
The Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) Study is a longitudinal neuroimaging study of unprecedented scale that is in the process of following over 11,000 youth from middle childhood though age 20. However, a design feature of the study's stop-signal task violates "context independence", an assumption critical to current non-parametric methods for estimating stop-signal reaction time (SSRT), a key measure of inhibitory ability in the study. This has led some experts to call for the task to be changed and for previously collected data to be used with caution. We present a cognitive process modeling framework, the RDEX-ABCD model, that provides a parsimonious explanation for the impact of this design feature on "go" stimulus processing and successfully accounts for key behavioral trends in the ABCD data. Simulation studies using this model suggest that failing to account for the context independence violations in the ABCD design can lead to erroneous inferences in several realistic scenarios. However, we demonstrate that RDEX-ABCD effectively addresses these violations and can be used to accurately measure SSRT along with an array of additional mechanistic parameters of interest (e.g., attention to the stop signal, cognitive efficiency), advancing investigators' ability to draw valid and nuanced inferences from ABCD data. AVAILABILITY OF DATA AND MATERIALS: Data from the ABCD Study are available through the NIH Data Archive (NDA): nda.nih.gov/abcd. Code for all analyses featured in this study is openly available on the Open Science Framework (OSF): osf.io/2h8a7/.
Keywords: Bayesian cognitive modeling; Evidence accumulation; Inhibition; Parameter recovery; Trigger failure.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Ando T. Predictive Bayesian model selection. Am. J. Math. Manag. Sci. 2011;31(1–2):13–38.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U24 DA041147/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA051039/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041120/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA051018/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041093/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DA041123/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DA051561/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA051037/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA051016/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041106/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041117/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041148/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041174/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AA007477/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA051038/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041134/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041022/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041156/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA050987/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041025/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA050989/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041089/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA050988/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041028/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041048/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

