ATR Inhibition in Advanced Urothelial Carcinoma
- PMID: 36604210
- PMCID: PMC10750798
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clgc.2022.10.016
ATR Inhibition in Advanced Urothelial Carcinoma
Abstract
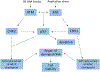
The ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related (ATR) checkpoint kinase 1 (CHK1) pathway is intricately involved in protecting the integrity of the human genome by suppressing replication stress and repairing DNA damage. ATR is a promising therapeutic target in cancer cells because its inhibition could lead to an accumulation of damaged DNA preventing further replication and division. ATR inhibition is being studied in multiple types of cancer, including advanced urothelial carcinoma where there remains an unmet need for novel therapies to improve outcomes. Herein, we review preclinical and clinical data evaluating 4 ATR inhibitors as monotherapy or in combination with chemotherapy. The scope of this review is focused on contemporary studies evaluating the application of this novel therapy in advanced urothelial carcinoma.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors have no conflicts of interest to report
Figures

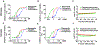
References
-
- von der Maase H, Sengelov L, Roberts JT, et al. Long-term survival results of a randomized trial comparing gemcitabine plus cisplatin, with methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin, plus cisplatin in patients with bladder cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:4602–4608. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.07.757. - DOI - PubMed
-
- von der Maase H, Hansen SW, Roberts JT, et al. Gemcitabine and cisplatin versus methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin, and cisplatin in advanced or metastatic bladder cancer: results of a large, randomized, multinational, multicenter, phase III study. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:3068–3077. - PubMed
-
- Cancer Stat Facts: Bladder Cancer. NIH NCI: surveillance, epidemiology, and end results program. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/urinb.html. Published 2019. Accessed August 11, 2021.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

