Identification of faecal extracellular vesicles as novel biomarkers for the non-invasive diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer
- PMID: 36604402
- PMCID: PMC9816085
- DOI: 10.1002/jev2.12300
Identification of faecal extracellular vesicles as novel biomarkers for the non-invasive diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer
Abstract
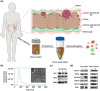
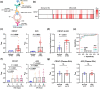
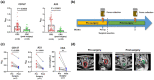
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most common malignancies that is usually detected late in the clinic. The currently available diagnostic tools for CRC are either invasive or insensitive to early lesions due to the dearth of reliable biomarkers. In this study, we discovered that the extracellular vesicles (EVs) in the faeces of CRC patients can act as a potent biomarker for the non-invasive diagnosis and prognosis of CRC. This finding is based on the identification of two transmembrane proteins-CD147 and A33-on faeces-derived EVs (fEVs) that are intrinsically associated with CRC. The detection results show that the levels of CD147 and A33 on fEVs were upregulated in the CRC patients (n = 48), dramatically distinguishing them from the healthy donors (n = 16). The CD147/A33-enriched EVs offer a clinical sensitivity of 89%, much higher than that (40%) of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), a clinically-established serum biomarker for CRC diagnosis. In addition, the analysis of longitudinal faeces samples (n = 29) demonstrated that the CD147/A33-enriched fEVs can be utilized to track the prognosis of CRC. Due to the high compliance of faeces-based detection, the CD147/A33-enriched fEVs could serve as new-generation CRC biomarkers for large-scale, non-invasive CRC screening as well as real-time monitoring of patient outcomes during clinical interventions.
Keywords: biomarkers; clinical diagnosis; colorectal cancer; extracellular vesicles; faeces.
© 2023 The Authors. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles published by Wiley Periodicals, LLC on behalf of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Alvarez, M. L. , Khosroheidari, M. , Kanchi Ravi, R. , & Distefano, J. K. (2012). Comparison of protein, microRNA, and mRNA yields using different methods of urinary exosome isolation for the discovery of kidney disease biomarkers. Kidney International, 82, 1024–1032. - PubMed
-
- Cavalera, S. , Russo, A. , Foglia, E. A. , Grazioli, S. , Colitti, B. , Rosati, S. , Nogarol, C. , Di Nardo, F. , Serra, T. , Chiarello, M. , Baggiani, C. , Pezzoni, G. , Brocchi, E. , & Anfossi, L. (2022). Design of multiplexing lateral flow immunoassay for detection and typing of foot‐and‐mouth disease virus using pan‐reactive and serotype‐specific monoclonal antibodies: Evidence of a new hook effect. Talanta, 240, 123155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

