Coordinated reprogramming of renal cancer transcriptome, metabolome and secretome associates with immune tumor infiltration
- PMID: 36604669
- PMCID: PMC9814214
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-022-02845-y
Coordinated reprogramming of renal cancer transcriptome, metabolome and secretome associates with immune tumor infiltration
Abstract
Background: Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is the most common subtype of renal cancer. The molecules (proteins, metabolites) secreted by tumors affect their extracellular milieu to support cancer progression. If secreted in amounts detectable in plasma, these molecules can also serve as useful, minimal invasive biomarkers. The knowledge of ccRCC tumor microenvironment is fragmentary. In particular, the links between ccRCC transcriptome and the composition of extracellular milieu are weakly understood. In this study, we hypothesized that ccRCC transcriptome is reprogrammed to support alterations in tumor microenvironment. Therefore, we comprehensively analyzed ccRCC extracellular proteomes and metabolomes as well as transcriptomes of ccRCC cells to find molecules contributing to renal tumor microenvironment.
Methods: Proteomic and metabolomics analysis of conditioned media isolated from normal kidney cells as well as five ccRCC cell lines was performed using mass spectrometry, with the following ELISA validation. Transcriptomic analysis was done using microarray analysis and validated using real-time PCR. Independent transcriptomic and proteomic datasets of ccRCC tumors were used for the analysis of gene and protein expression as well as the level of the immune infiltration.
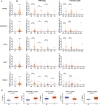
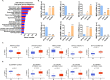
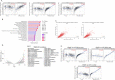
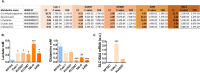
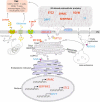
Results: Renal cancer secretome contained 85 proteins detectable in human plasma, consistently altered in all five tested ccRCC cell lines. The top upregulated extracellular proteins included SPARC, STC2, SERPINE1, TGFBI, while downregulated included transferrin and DPP7. The most affected extracellular metabolites were increased 4-hydroxy-proline, succinic acid, cysteine, lactic acid and downregulated glutamine. These changes were associated with altered expression of genes encoding the secreted proteins (SPARC, SERPINE1, STC2, DPP7), membrane transporters (SLC16A4, SLC6A20, ABCA12), and genes involved in protein trafficking and secretion (KIF20A, ANXA3, MIA2, PCSK5, SLC9A3R1, SYTL3, and WNTA7). Analogous expression changes were found in ccRCC tumors. The expression of SPARC predicted the infiltration of ccRCC tumors with endothelial cells. Analysis of the expression of the 85 secretome genes in > 12,000 tumors revealed that SPARC is a PanCancer indicator of cancer-associated fibroblasts' infiltration.
Conclusions: Transcriptomic reprogramming of ccRCC supports the changes in an extracellular milieu which are associated with immune infiltration. The proteins identified in our study represent valuable cancer biomarkers detectable in plasma.
Keywords: CAFs; Immune infiltration; Metabolome; Renal cancer; SPARC; Secretome.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Secretome profiling of oral squamous cell carcinoma-associated fibroblasts reveals organization and disassembly of extracellular matrix and collagen metabolic process signatures.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jul;37(7):9045-57. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4629-y. Epub 2016 Jan 13. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26762409
-
PYCR1 regulates glutamine metabolism to construct an immunosuppressive microenvironment for the progression of clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Am J Cancer Res. 2022 Aug 15;12(8):3780-3798. eCollection 2022. Am J Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36119844 Free PMC article.
-
Global Characterization of Immune Infiltration in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Onco Targets Ther. 2021 Mar 22;14:2085-2100. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S282763. eCollection 2021. Onco Targets Ther. 2021. PMID: 33790572 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular milieu in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 14;12:943583. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.943583. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36313721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer secretome: finding out hidden messages in extracellular secretions.Clin Transl Oncol. 2023 May;25(5):1145-1155. doi: 10.1007/s12094-022-03027-y. Epub 2022 Dec 16. Clin Transl Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36525229 Review.
Cited by
-
Computational Characterization of Membrane Proteins as Anticancer Targets: Current Challenges and Opportunities.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 26;25(7):3698. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073698. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612509 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of Heat Shock-Induced H3K9ac Reduction Sensitizes Cancer Cells to Hyperthermia.Int J Biol Sci. 2023 Sep 11;19(15):4849-4864. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.86384. eCollection 2023. Int J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37781518 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Amplifies the Immunogenicity of Healthy Renal Epithelium in the Presence of Renal Cell Carcinoma.Cells. 2024 Dec 10;13(24):2038. doi: 10.3390/cells13242038. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39768130 Free PMC article.
-
DPP7 Promotes Colorectal Cancer Progression Through GPX4-Dependent Suppression of Disulfidptosis and Immune Evasion.J Cell Mol Med. 2025 Jun;29(12):e70660. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70660. J Cell Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40576169 Free PMC article.
-
SPARC: a key mediator of apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells and its role in hypertension mechanism.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2025 Apr;61(4):374-388. doi: 10.1007/s11626-025-01026-1. Epub 2025 Apr 14. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2025. PMID: 40229525
References
-
- Peinado H, Zhang H, Matei IR, Costa-Silva B, Hoshino A, Rodrigues G, et al. Pre-metastatic niches: organ-specific homes for metastases. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017;17(5):302–317. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

