Full-length transcriptome and metabolite analysis reveal reticuline epimerase-independent pathways for benzylisoquinoline alkaloids biosynthesis in Sinomenium acutum
- PMID: 36605968
- PMCID: PMC9808091
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1086335
Full-length transcriptome and metabolite analysis reveal reticuline epimerase-independent pathways for benzylisoquinoline alkaloids biosynthesis in Sinomenium acutum
Abstract
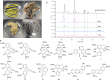
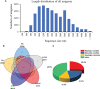
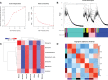
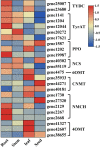
Benzylisoquinoline alkaloids (BIAs) are a large family of plant natural products with important pharmaceutical applications. Sinomenium acutum is a medicinal plant from the Menispermaceae family and has been used to treat rheumatoid arthritis for hundreds of years. Sinomenium acutum contains more than 50 BIAs, and sinomenine is a representative BIA from this plant. Sinomenine was found to have preventive and curative effects on opioid dependence. Despite the broad applications of S. acutum, investigation on the biosynthetic pathways of BIAs from S. acutum is limited. In this study, we comprehensively analyzed the transcriptome data and BIAs in the root, stem, leaf, and seed of S. acutum. Metabolic analysis showed a noticeable difference in BIA contents in different tissues. Based on the study of the full-length transcriptome, differentially expressed genes, and weighted gene co-expression network, we proposed the biosynthetic pathways for a few BIAs from S. acutum, such as sinomenine, magnoflorine, and tetrahydropalmatine, and screened candidate genes involved in these biosynthesis processes. Notably, the reticuline epimerase (REPI/STORR), which converts (S)-reticuline to (R)-reticuline and plays an essential role in morphine and codeine biosynthesis, was not found in the transcriptome data of S. acutum. Our results shed light on the biogenesis of the BIAs in S. acutum and may pave the way for the future development of this important medicinal plant.
Keywords: Sinomenium acutum; benzylisoquinoline alkaloid; biosynthetic pathway; transcriptome; weighted gene co-expression network analysis.
Copyright © 2022 Yang, Sun, Wang, Yin, Sun, Xue, Huang, Wang and Yan.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Ying Sun was employed by the company WuXi App Tec (Tianjin) Co. Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commerical or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

